Unveiling Scotland’s Respiratory Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Air Quality Mapping
Related Articles: Unveiling Scotland’s Respiratory Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Air Quality Mapping
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Scotland’s Respiratory Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Air Quality Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Scotland’s Respiratory Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Air Quality Mapping
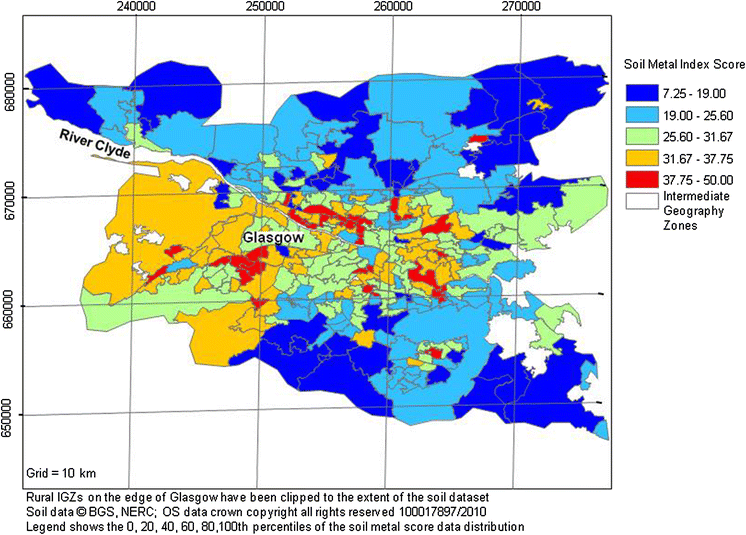
Scotland, with its breathtaking landscapes and vibrant cities, faces a growing challenge: maintaining the quality of its air. While the country boasts a reputation for clean air, the reality is more nuanced. Air pollution, an invisible threat, can have serious consequences for human health and the environment. To understand this intricate interplay, Scotland relies on a powerful tool: air quality mapping. This intricate network of data points and visualizations provides a comprehensive picture of air quality across the nation, revealing the areas most vulnerable to pollution and the sources contributing to it.
A Visual Representation of Breath: Understanding the Air Quality Map of Scotland
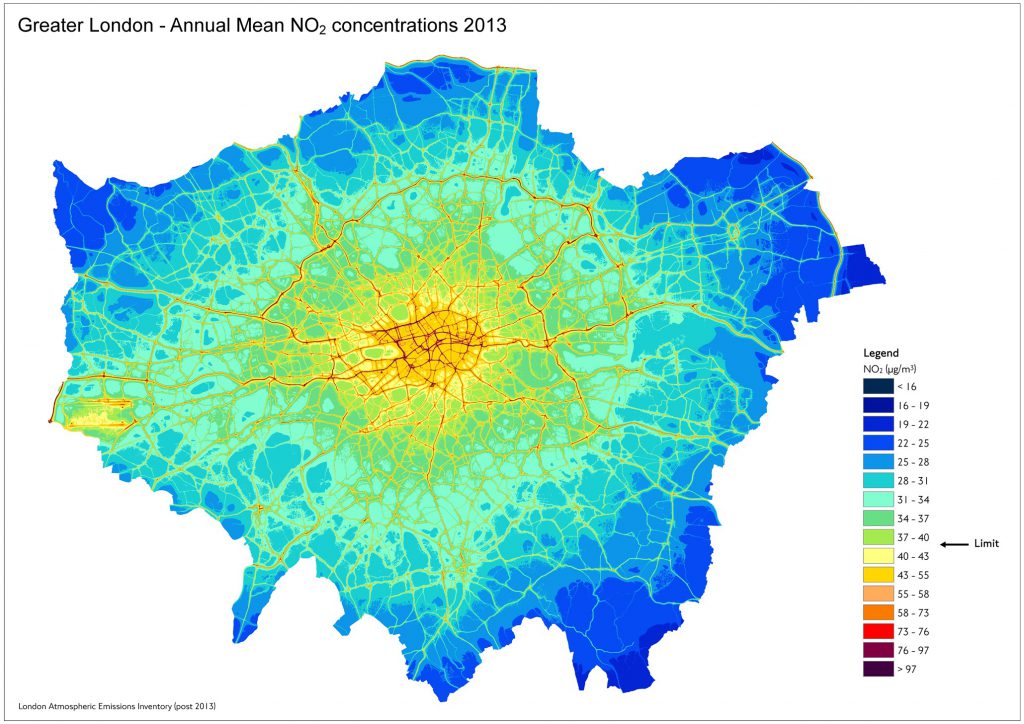
The air quality map of Scotland is not just a collection of colors and numbers; it is a window into the invisible forces shaping the air we breathe. It utilizes a complex system of monitoring stations strategically placed across the country, collecting data on various pollutants like nitrogen dioxide (NO2), particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), ozone (O3), and sulfur dioxide (SO2). This data is then processed and visualized on a map, using color gradients to illustrate the concentration levels of these pollutants in different areas.
The map allows for a clear understanding of:
- Spatial Distribution: Identifying areas with high and low concentrations of pollutants, pinpointing hotspots and areas where pollution levels are within safe limits.
- Temporal Trends: Tracking changes in pollution levels over time, revealing seasonal variations, long-term trends, and the impact of specific events like traffic congestion or industrial activity.
- Source Identification: Relating pollution levels to specific sources, such as traffic, industrial emissions, domestic heating, or agricultural practices. This information is crucial for developing targeted strategies to mitigate pollution.
Beyond the Map: The Vital Role of Air Quality Monitoring
The air quality map is not a static entity; it is a dynamic tool constantly evolving with the influx of real-time data. This constant monitoring is essential for several reasons:
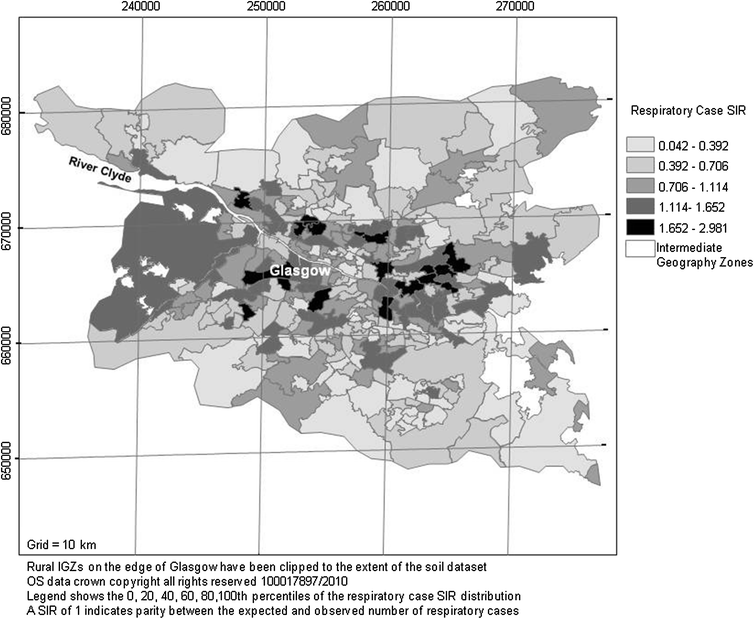
- Public Health: Air pollution is a significant health risk, contributing to respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and even premature mortality. By identifying areas with elevated pollution levels, public health authorities can implement targeted interventions and awareness campaigns to protect vulnerable populations.
- Environmental Impact: Air pollution has adverse effects on ecosystems, contributing to acid rain, damaging vegetation, and impacting biodiversity. The map allows researchers and environmental agencies to monitor these impacts and develop strategies for mitigating pollution’s effects on the natural environment.
- Policy Development: The data collected through air quality monitoring informs policy decisions related to air quality management. By understanding the sources and patterns of pollution, policymakers can implement effective regulations, promote cleaner technologies, and incentivize sustainable practices.
Unveiling the Contributors: A Closer Look at Pollution Sources in Scotland
While the air quality map provides a comprehensive overview, understanding the specific sources of pollution is crucial for effective mitigation. Here are some key contributors to air pollution in Scotland:
- Road Transport: Vehicles, particularly diesel engines, are a major source of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter. Traffic congestion in urban areas significantly exacerbates this problem.
- Industrial Emissions: Manufacturing, power generation, and other industrial processes release various pollutants, including sulfur dioxide (SO2), particulate matter, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- Domestic Heating: Burning coal and wood for heating releases significant amounts of particulate matter and other pollutants, particularly in rural areas during winter.
- Agriculture: Agricultural practices, such as livestock farming and fertilizer use, contribute to emissions of ammonia (NH3) and other pollutants.
The Future of Air Quality in Scotland: A Call for Collective Action
Improving air quality in Scotland is a shared responsibility, requiring collaboration between government agencies, businesses, and individuals. The air quality map acts as a crucial tool in this endeavor, providing data that can inform:
- Policy Interventions: Developing and implementing stricter emission standards for vehicles, industries, and domestic heating systems.
- Technological Innovations: Promoting cleaner technologies, such as electric vehicles, renewable energy sources, and efficient industrial processes.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public about the health risks of air pollution and promoting sustainable practices, such as walking, cycling, and using public transportation.
Frequently Asked Questions about Air Quality Mapping in Scotland
Q: Where can I find the air quality map for Scotland?
A: The Scottish Environment Protection Agency (SEPA) provides an interactive air quality map on its website, which displays real-time data and historical trends.
Q: What are the different pollutants monitored by the air quality map?
A: The map monitors several pollutants, including nitrogen dioxide (NO2), particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), ozone (O3), and sulfur dioxide (SO2).
Q: How often is the air quality data updated?
A: The data is updated in real-time, with some stations providing hourly readings.
Q: How can I contribute to improving air quality in Scotland?
A: You can contribute by:
- Choosing sustainable transport: Walking, cycling, or using public transport instead of driving.
- Reducing energy consumption: Using energy-efficient appliances and reducing heating and cooling needs.
- Supporting clean energy: Advocating for renewable energy sources and supporting businesses committed to sustainable practices.
- Staying informed: Monitoring air quality data and participating in public consultations on air quality management.
Tips for Navigating the Air Quality Map of Scotland
- Understand the color scale: Familiarize yourself with the color gradient used on the map to interpret the concentration levels of different pollutants.
- Zoom in on specific areas: Use the zoom function to explore air quality in your neighborhood or a particular city.
- Explore historical data: Use the time slider to view air quality trends over different periods.
- Identify potential sources: Use the map to identify potential sources of pollution near your home or workplace.
- Share your findings: Spread awareness about air quality issues and encourage others to use the map.
Conclusion: A Collective Effort for a Breath of Fresh Air
The air quality map of Scotland is not just a tool for monitoring; it is a catalyst for action. By providing a comprehensive understanding of the state of our air, it empowers us to make informed decisions, adopt sustainable practices, and work collectively to ensure a healthier future for generations to come. As we continue to monitor and address the challenges of air pollution, the air quality map will remain a vital resource, guiding us towards a cleaner, greener, and healthier Scotland.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Scotland’s Respiratory Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Air Quality Mapping. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
