Unveiling the Essence of Scale in Cartography: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: Unveiling the Essence of Scale in Cartography: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Essence of Scale in Cartography: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Essence of Scale in Cartography: A Comprehensive Exploration

Maps, the visual representations of our planet, are indispensable tools for understanding and navigating the world. They condense the vastness of Earth onto a manageable surface, enabling us to comprehend spatial relationships and make informed decisions. However, the accuracy and clarity of a map hinge upon a crucial element: scale.
Defining the Essence of Scale in Cartography:
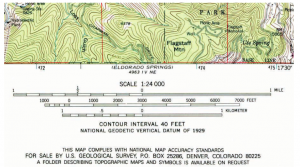
Scale in cartography refers to the ratio between the distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. It dictates the level of detail a map can portray and determines the extent of the area it encompasses. Understanding scale is paramount for interpreting maps effectively and accurately.
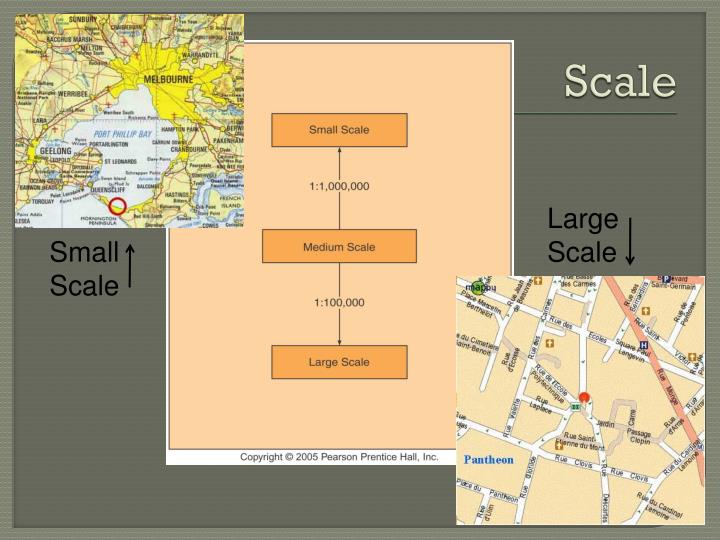
Types of Map Scales:
There are three primary ways to express map scale:
- Verbal Scale: This straightforward method uses words to state the relationship between map distance and ground distance. For instance, "1 centimeter on the map represents 1 kilometer on the ground."
- Representative Fraction (RF): This numerical scale uses a fraction to express the ratio. For example, 1:100,000 indicates that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units on the ground.
- Graphic Scale: A graphic scale, often depicted as a bar, visually represents the scale using a line divided into segments corresponding to specific distances on the ground. This method provides a quick and intuitive reference for measuring distances directly on the map.
The Significance of Scale in Map Interpretation:
Scale plays a pivotal role in map interpretation, impacting several key aspects:
- Level of Detail: Maps with larger scales (e.g., 1:10,000) represent smaller areas but display greater detail, revealing intricate features like individual buildings or roads. Conversely, smaller scales (e.g., 1:10,000,000) encompass vast regions but depict only major features like national borders or large cities.
- Accuracy: Scale influences the accuracy of map representations. Larger-scale maps provide more precise measurements and depict features more accurately.
- Purpose: The choice of scale depends on the map’s intended purpose. For instance, a detailed city map would use a larger scale to showcase urban infrastructure, while a world map would employ a smaller scale to depict global patterns.
The Importance of Scale in Geographic Analysis:
Scale is not merely a technical aspect of map-making; it is a fundamental concept in geographic analysis. It emphasizes the crucial role of spatial context in understanding phenomena. Geographers recognize that processes and patterns vary across different scales. For example, analyzing urban sprawl requires a different scale than studying global climate change.
Scale and the Challenge of Generalization:
Maps are inherently simplified representations of reality. The process of generalization, the selective inclusion and exclusion of information, is influenced by scale. Larger-scale maps can include more detail, while smaller-scale maps necessitate generalization to avoid overcrowding. This process involves:
- Selection: Choosing which features to depict based on their relevance and importance at the chosen scale.
- Simplification: Reducing the complexity of features by omitting minor details or using symbols to represent complex objects.
- Displacement: Shifting features slightly to avoid overlap or distortion.
Scale and the Evolution of Cartography:
The development of technology has significantly impacted the way scale is utilized in cartography. Digital mapping tools allow for dynamic scaling, enabling users to zoom in and out of maps seamlessly. This interactive approach offers unprecedented flexibility and enhances the understanding of spatial relationships.
FAQs: Delving Deeper into Map Scale:
Q: What is the difference between a large-scale map and a small-scale map?
A: A large-scale map represents a smaller area with greater detail, while a small-scale map encompasses a larger area but depicts fewer features.
Q: How do I determine the scale of a map?
A: Look for the verbal scale, representative fraction, or graphic scale provided on the map.
Q: What are the implications of using the wrong scale for a particular task?
A: Using an inappropriate scale can lead to inaccurate measurements, misinterpretations of features, and flawed conclusions.
Q: Can a map have multiple scales?
A: Yes, some maps may incorporate multiple scales to depict different aspects of a region or to cater to diverse user needs.
Tips for Effective Map Interpretation:
- Always pay attention to the scale: Before interpreting any map, ensure you understand the scale it uses.
- Consider the map’s purpose: The scale chosen reflects the map’s intended use.
- Use the graphic scale for accurate measurements: A graphic scale allows for quick and precise distance estimations.
- Be aware of generalization: Recognize that maps are simplified representations and consider the limitations of the chosen scale.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Scale in Geographic Understanding:
Scale is a fundamental concept in cartography, profoundly influencing map interpretation and geographic analysis. Understanding the relationship between map distance and ground distance allows for accurate measurements, informed decision-making, and a deeper comprehension of spatial patterns and processes. By embracing the power of scale, we gain a more nuanced and insightful perspective on the world around us.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Essence of Scale in Cartography: A Comprehensive Exploration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
