Unveiling the Essence of Scale in Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unveiling the Essence of Scale in Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Essence of Scale in Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Essence of Scale in Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
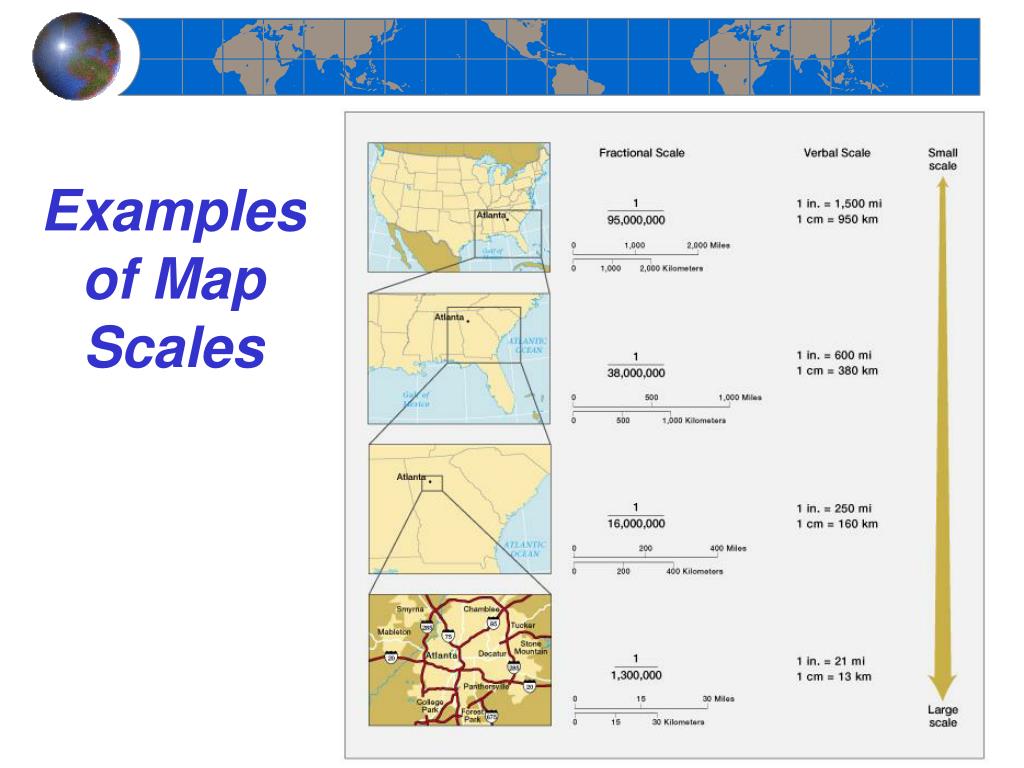
Maps are powerful tools, capable of condensing vast expanses of land into manageable representations. However, their utility hinges on an often overlooked element: scale. This fundamental concept dictates the relationship between distances on a map and their real-world counterparts, forming the bridge between the abstract and the tangible. Understanding map scale is crucial for accurately interpreting and utilizing maps in various disciplines, from navigation and exploration to environmental analysis and urban planning.
The Significance of Scale in Map Interpretation
Imagine a map depicting a sprawling city. The same map could be used to navigate a bustling downtown district or to locate a specific park on the outskirts. However, the clarity and effectiveness of this map would vary drastically depending on its scale. A map designed for navigating the entire city would likely show major roads and landmarks, omitting details like individual buildings or smaller streets. Conversely, a map focused on a specific neighborhood would showcase a higher level of detail, including individual buildings, parks, and local businesses.
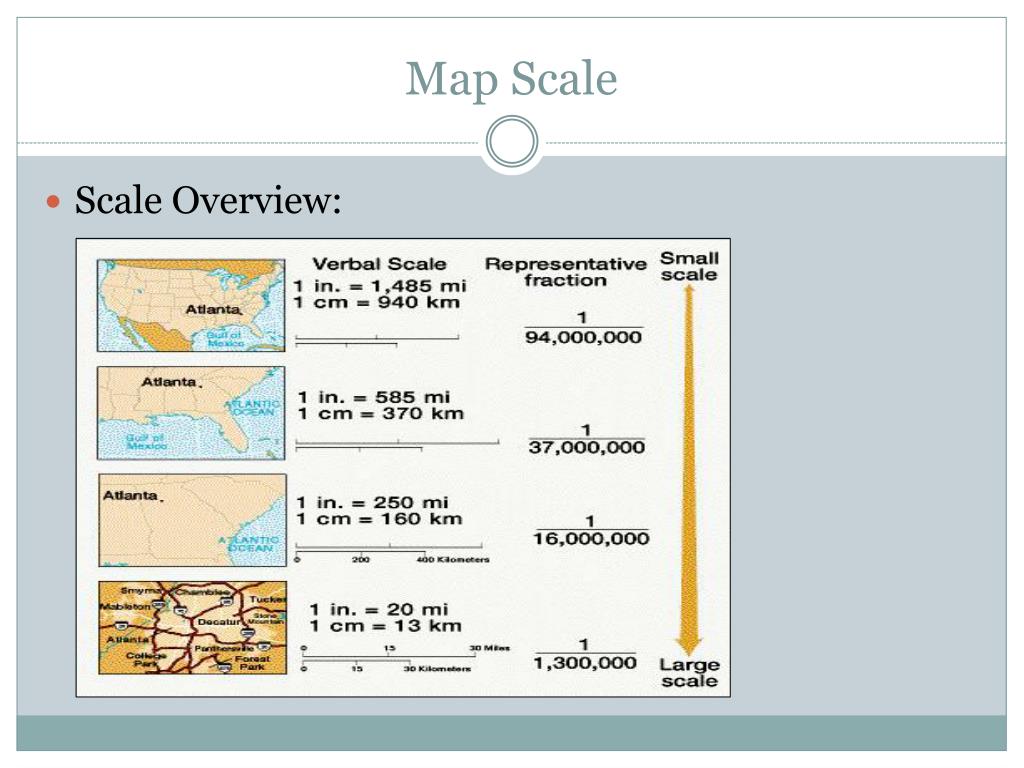
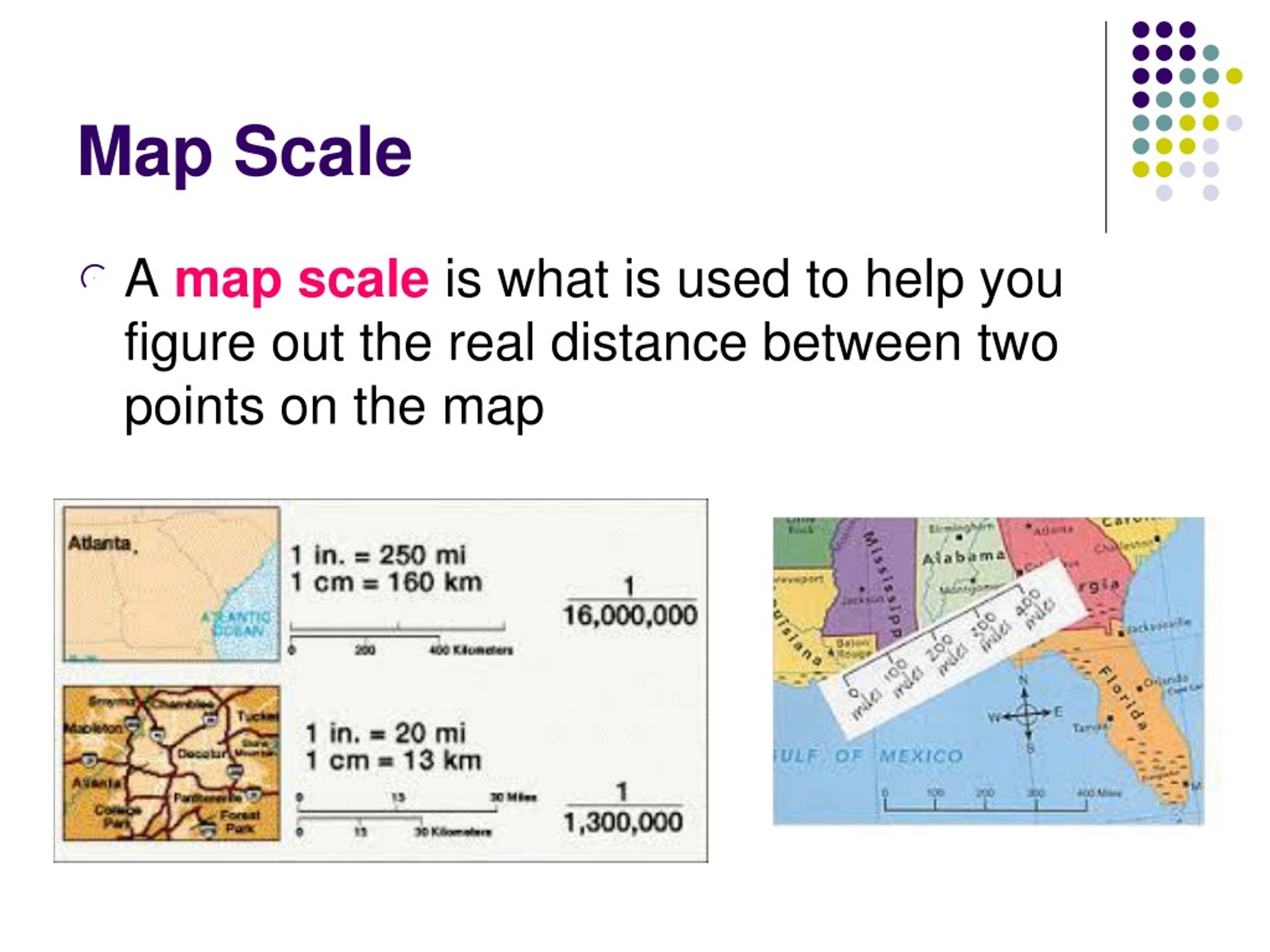
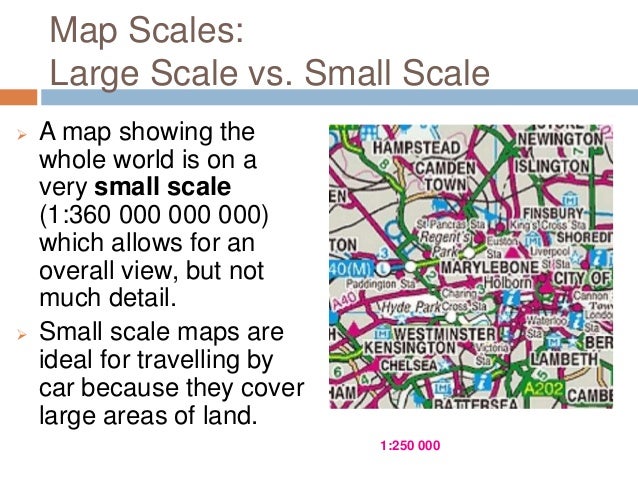
This example highlights the importance of scale in map interpretation. Scale determines the level of detail and the scope of information presented on a map. A large-scale map, characterized by a larger representative fraction (e.g., 1:1000), focuses on a smaller area with greater detail. Conversely, a small-scale map, with a smaller representative fraction (e.g., 1:100,000), encompasses a broader area but with less detail.
Types of Map Scales
Map scales are typically expressed in three primary ways:
-
Verbal Scale: This method uses words to describe the relationship between map distances and real-world distances. For instance, "1 centimeter on the map represents 1 kilometer in reality." While intuitive, verbal scales can be cumbersome and lack precision.
-
Representative Fraction (RF): This is the most common and precise method of expressing map scale. It is represented as a ratio, such as 1:100,000. This means that one unit on the map corresponds to 100,000 units in the real world. The RF remains constant regardless of the units used for measurement.
-
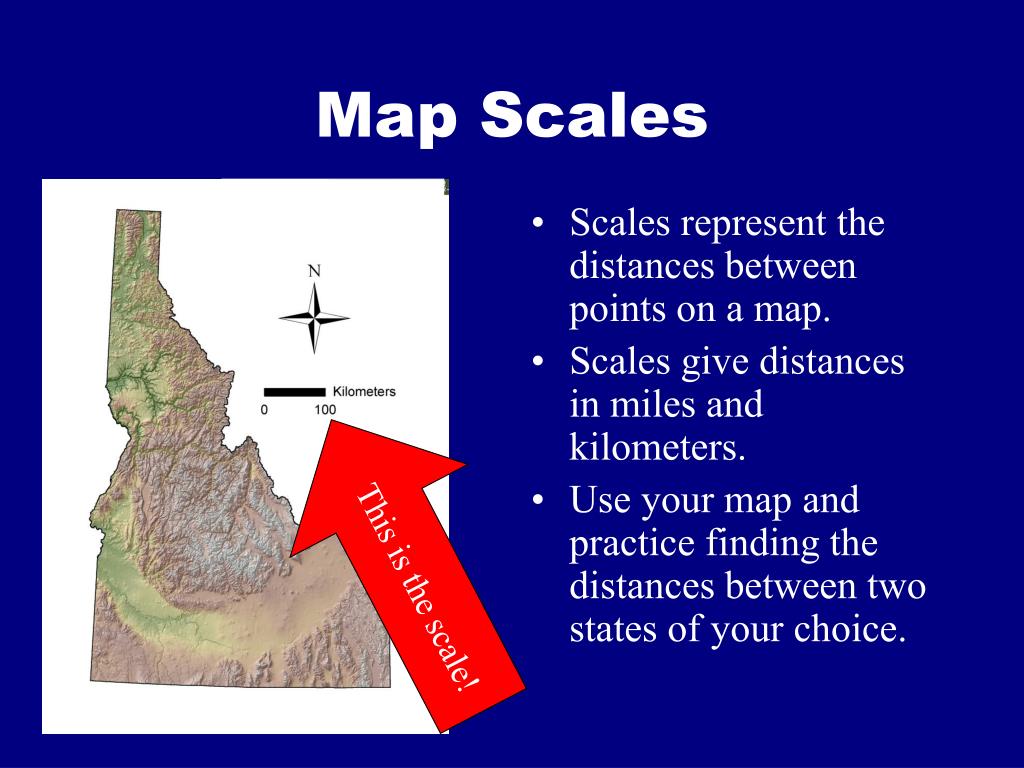
Graphic Scale: This method utilizes a visual representation of the scale, often in the form of a bar. The bar is divided into segments representing specific distances on the map. This allows for quick and easy measurement of distances directly on the map, even without knowing the exact RF.
Understanding and Utilizing Map Scale
To effectively utilize maps, it is essential to understand the scale and its implications. Here are some key points to consider:
-
Scale influences the level of detail: A larger scale map will show more detail, while a smaller scale map will provide a broader overview.
-
Scale dictates the suitability of a map for a specific purpose: A map designed for navigating a city would be unsuitable for planning a hiking trip in a remote area.
-
Scale impacts the accuracy of measurements: A large-scale map allows for more precise measurements than a small-scale map.
-
Scale can be used to estimate distances on a map: By understanding the RF, you can calculate real-world distances from map measurements.
Beyond Traditional Map Scales: Digital Mapping and Scale
The advent of digital mapping has brought about new dimensions to the concept of scale. While traditional paper maps rely on fixed scales, digital maps offer greater flexibility. Users can zoom in and out, effectively changing the scale on demand. This dynamic scaling allows for a seamless transition between detailed views of specific locations and broader overviews of larger areas.
However, the principles of scale remain fundamental even in digital mapping. The underlying data and the resolution of the digital map determine the level of detail that can be displayed at different zoom levels. Understanding the scale at which a digital map is being viewed is crucial for accurate interpretation and analysis.
Applications of Map Scale in Diverse Fields
Map scale plays a crucial role in a wide range of disciplines, including:
-
Navigation and Exploration: Navigating unfamiliar terrain requires maps with appropriate scales to show relevant landmarks, trails, and obstacles.
-
Urban Planning and Development: Planning and designing urban environments necessitates maps with detailed representations of streets, buildings, and infrastructure.
-
Environmental Analysis and Management: Understanding spatial patterns and distribution of natural resources, pollution, and other environmental factors requires maps with varying scales to analyze different levels of detail.
-
Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS utilizes spatial data and maps with varying scales to analyze and visualize complex geographic phenomena.
-
Cartography and Mapmaking: Cartographers rely on scale to create accurate and informative maps that effectively convey geographic information.
FAQs Regarding Map Scale
Q: What is the difference between a large-scale map and a small-scale map?
A: A large-scale map depicts a smaller area with greater detail, while a small-scale map shows a larger area with less detail. The difference is determined by the representative fraction (RF). A larger RF indicates a smaller area and greater detail, while a smaller RF represents a larger area and less detail.
Q: How can I calculate distances on a map?
A: You can calculate distances on a map using the representative fraction (RF). Measure the distance on the map and multiply it by the denominator of the RF. For example, if the RF is 1:100,000 and you measure a distance of 5 centimeters on the map, the real-world distance would be 5 cm * 100,000 = 500,000 centimeters, or 5 kilometers.
Q: How does scale impact the accuracy of measurements on a map?
A: A larger scale map allows for more precise measurements because it shows more detail. Conversely, a smaller scale map will result in less accurate measurements due to the reduced level of detail.
Q: What is the significance of scale in digital mapping?
A: Digital mapping allows for dynamic scaling, enabling users to zoom in and out to view areas at different levels of detail. However, the underlying data and resolution of the digital map determine the level of detail that can be displayed at different zoom levels.
Tips for Effective Use of Map Scale
-
Always check the scale of a map before using it. This will ensure that the map is appropriate for your intended purpose.
-
Understand the relationship between scale and detail. A larger scale map will provide more detail, while a smaller scale map will offer a broader overview.
-
Utilize graphic scales to quickly measure distances on a map. Graphic scales provide a visual representation of the scale and allow for easy measurement without calculating the RF.
-
Be aware of the limitations of scale. Even with a large-scale map, certain features may be omitted due to the limitations of the scale.
-
Consider the purpose of the map when choosing a scale. Different scales are suitable for different applications, such as navigation, planning, or analysis.
Conclusion
Map scale is a fundamental concept that underpins the accuracy and utility of maps. Understanding scale is essential for interpreting maps effectively, extracting meaningful information, and making informed decisions based on geographic data. Whether navigating a city, planning a hiking trip, or analyzing environmental patterns, the scale of a map plays a crucial role in shaping our understanding of the world around us. By recognizing the significance of scale, we can harness the power of maps to navigate, explore, and interpret the complexities of our planet.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Essence of Scale in Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
