Unveiling the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Topographic Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Topographic Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Topographic Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Topographic Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Topographic Maps
- 3.1 Decoding the Forked Run: A Visual Journey through River Systems
- 3.2 Beyond the Lines: Unveiling the Story of a River
- 3.3 Applications of Forked Run Topographic Maps: A Multifaceted Tool
- 3.4 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.5 Tips for Utilizing Forked Run Topographic Maps
- 3.6 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Visualization
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Topographic Maps
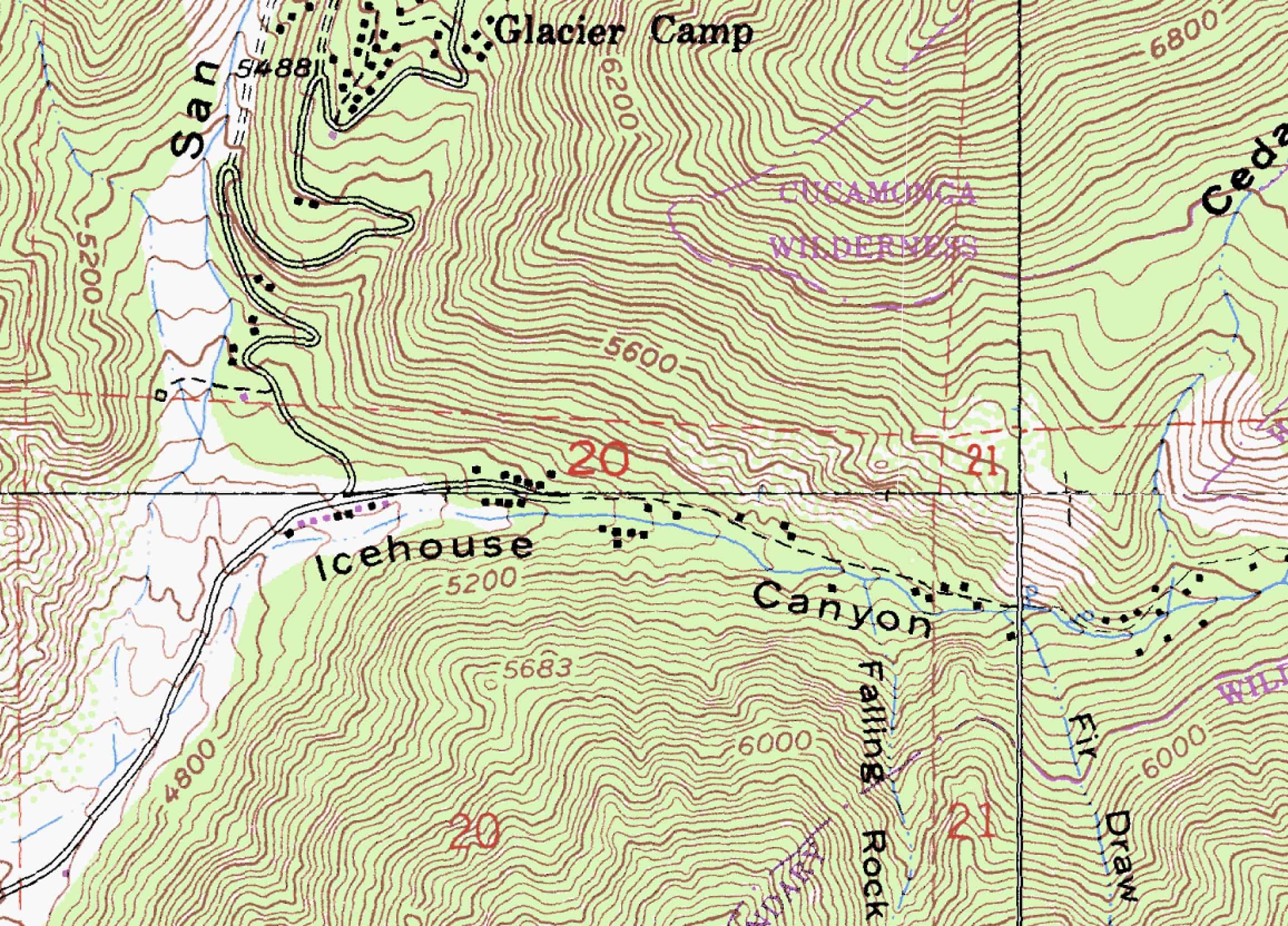
Topographic maps are essential tools for understanding and navigating the Earth’s surface. They provide a visual representation of the terrain, highlighting elevation changes, geographical features, and man-made structures. This detailed portrayal of the land’s form and shape is crucial for various applications, from planning outdoor adventures to conducting scientific research.
One specific type of topographic map, known as a "forked run" map, is particularly valuable for understanding the intricate details of river systems and their surrounding landscapes. These maps, characterized by their depiction of branching river channels, offer insights into the dynamic interplay between water flow, erosion, and landform development.
Decoding the Forked Run: A Visual Journey through River Systems
A forked run topographic map, at its core, is a visual representation of a river’s journey. It depicts the river’s main channel, known as the "trunk," and its various branches, or "forks," that extend outwards like the arms of a tree. These forks, often formed by natural processes like erosion and deposition, reveal the river’s history and its impact on the surrounding landscape.
The map’s contours, lines that connect points of equal elevation, play a crucial role in understanding the river’s path. They highlight the slopes and valleys that influence water flow, revealing areas where the river cuts deeply into the earth and where it spreads out across flatter terrain. The presence of waterfalls, rapids, and meanders are also evident, providing further insight into the river’s dynamic nature.
Beyond the Lines: Unveiling the Story of a River
Fork run maps go beyond simply showcasing the river’s physical form. They offer a window into the river’s history, revealing how it has sculpted the surrounding landscape over time. The map’s details can indicate areas of erosion, where the river has carved out deep channels and canyons, and areas of deposition, where sediment carried by the river has created fertile floodplains and deltas.
Furthermore, the map can reveal the impact of human activities on the river system. Evidence of dams, bridges, and agricultural practices can be observed, highlighting how human interventions have altered the river’s flow and the surrounding ecosystem.
Applications of Forked Run Topographic Maps: A Multifaceted Tool
Forked run topographic maps find applications in a wide range of fields, each leveraging their unique ability to provide detailed information about river systems:
- Hydrology and Geomorphology: These maps are invaluable for researchers studying river dynamics, erosion patterns, and the evolution of landscapes. They provide crucial data for understanding the relationship between water flow, sediment transport, and landform development.
- Environmental Management: Forked run maps are essential for assessing the impact of human activities on river systems. They help identify areas vulnerable to erosion, flooding, and pollution, enabling informed decision-making for sustainable management of water resources.
- Outdoor Recreation: Hikers, kayakers, and anglers utilize these maps to plan their adventures, identifying safe passageways, potential hazards, and promising fishing spots along the river.
- Urban Planning: Forked run maps play a vital role in urban planning by providing crucial information about flood risk, drainage systems, and potential land use limitations in areas adjacent to rivers.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: How are forked run topographic maps created?
A: Forked run topographic maps are typically created using a combination of aerial photography, satellite imagery, and ground surveys. These techniques allow for accurate measurement of elevations and the mapping of river channels and surrounding features.
Q: What are the limitations of forked run topographic maps?
A: Forked run topographic maps, while valuable, are not without limitations. They can be static representations of a dynamic system, meaning they don’t capture the constant changes occurring in a river system over time. Additionally, their accuracy can be limited by factors such as vegetation cover and the scale of the map.
Q: What are some alternatives to forked run topographic maps?
A: While forked run maps are highly useful, alternative tools exist for understanding river systems. These include:
- Digital Elevation Models (DEMs): These provide three-dimensional representations of the terrain, allowing for detailed analysis of elevation changes and river channels.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): This technology uses laser pulses to create highly accurate elevation data, providing a detailed picture of the river’s course and surrounding landscape.
- Remote Sensing: Satellite imagery and aerial photography can be used to monitor river flow, identify changes in vegetation, and assess the impact of human activities on the river system.
Tips for Utilizing Forked Run Topographic Maps
- Understanding the map’s scale: Pay attention to the map’s scale to accurately interpret the distances and sizes of features depicted.
- Identifying key features: Focus on the main channel, forks, contours, and any other relevant features that provide insight into the river’s characteristics.
- Interpreting elevation changes: Utilize the contour lines to understand the terrain’s slopes and valleys, which influence water flow and potential hazards.
- Considering the map’s limitations: Remember that forked run maps are static representations of a dynamic system. They should be used in conjunction with other data sources and field observations.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Visualization
Forked run topographic maps, with their detailed portrayal of river systems, offer a powerful tool for understanding the intricate relationship between water, land, and human activities. They serve as a foundation for informed decision-making in various fields, from environmental management to urban planning. By embracing the visual language of these maps, we gain a deeper appreciation for the dynamic processes that shape our planet and the importance of sustainable management for the future.



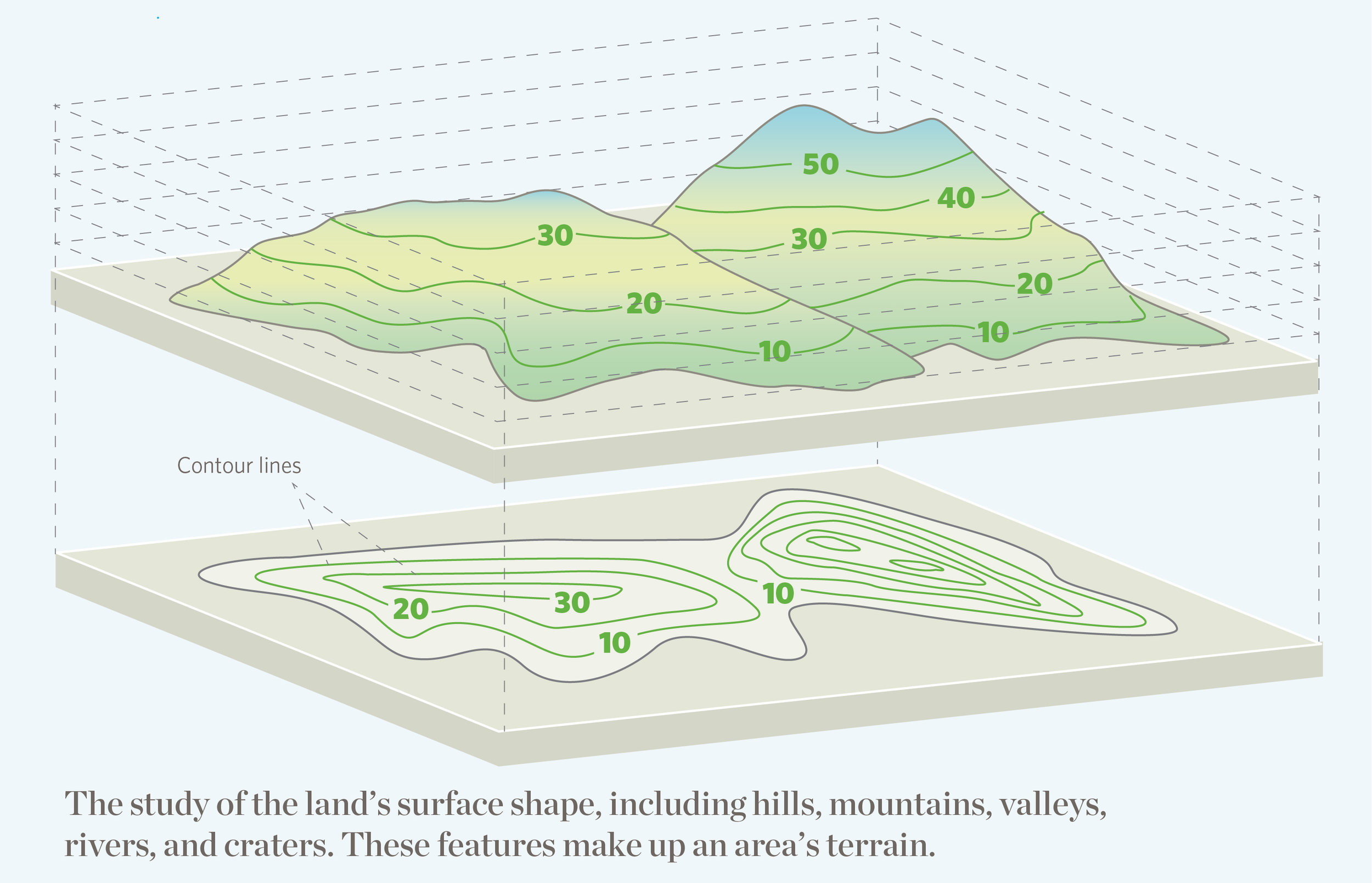

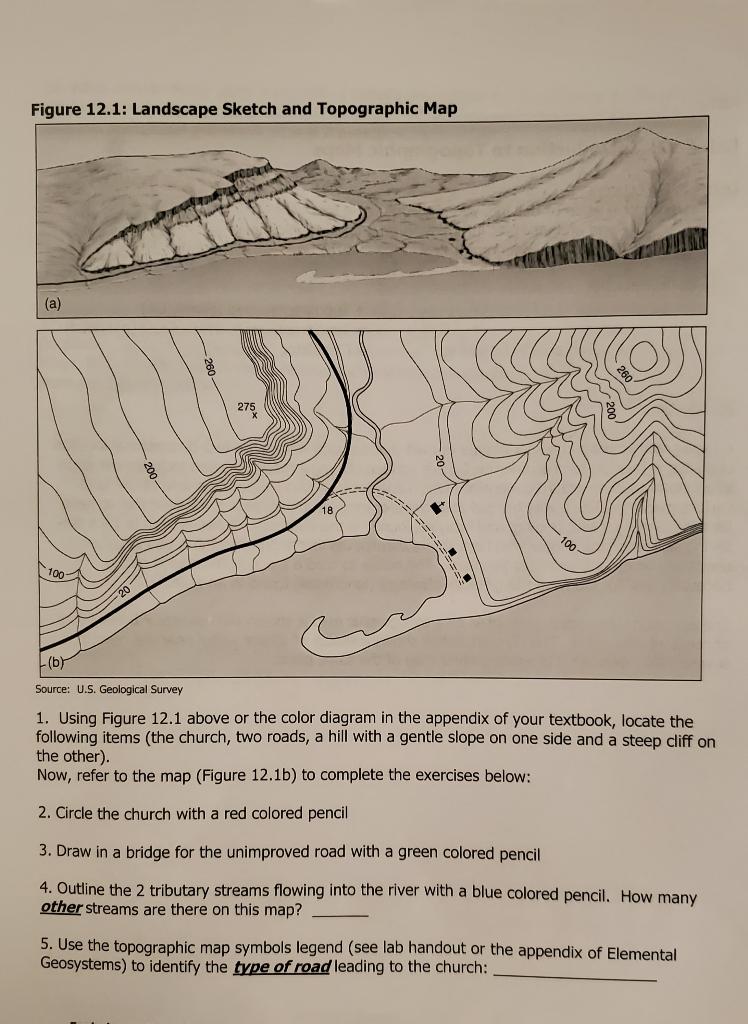
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Topographic Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
