Unveiling the Landscape: A Topographical Exploration of San Diego County
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Topographical Exploration of San Diego County
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Topographical Exploration of San Diego County. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: A Topographical Exploration of San Diego County

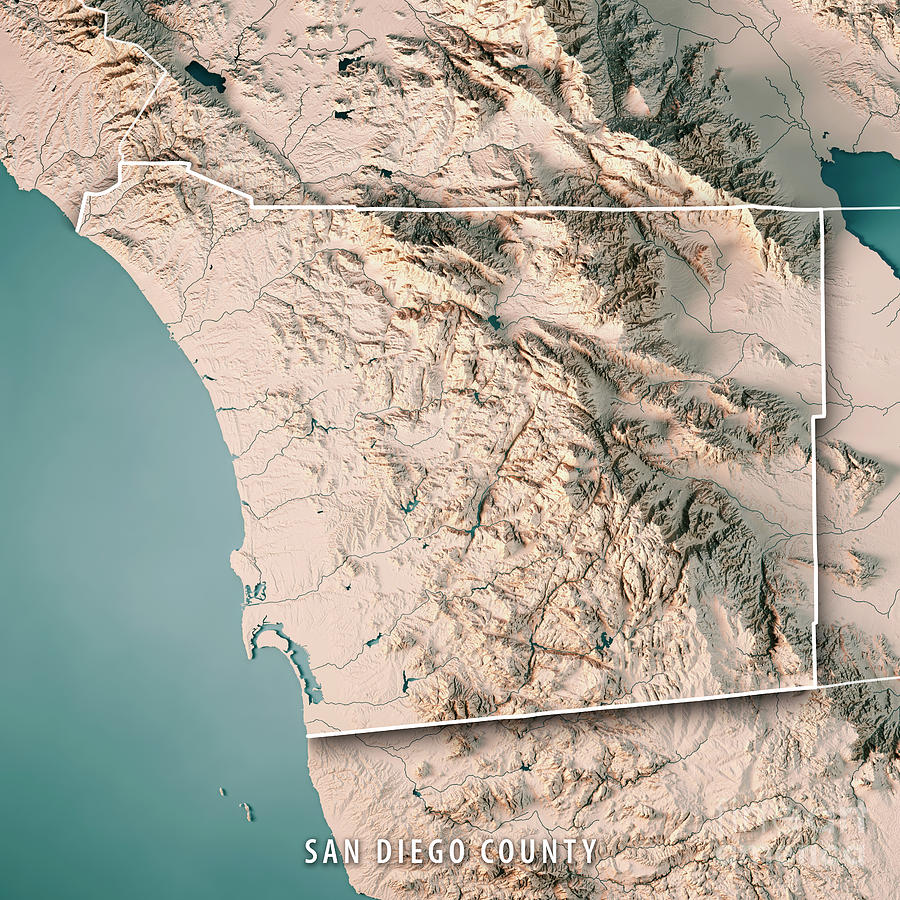
San Diego County, a vibrant tapestry of diverse ecosystems, boasts a topography as intricate and captivating as its human history. Understanding this landscape, with its rolling hills, rugged mountains, and coastal plains, is crucial for navigating its beauty, appreciating its ecological significance, and planning for its future. A topographical map serves as a key to unlocking this understanding, revealing the subtle nuances and dramatic shifts in elevation that shape the region.
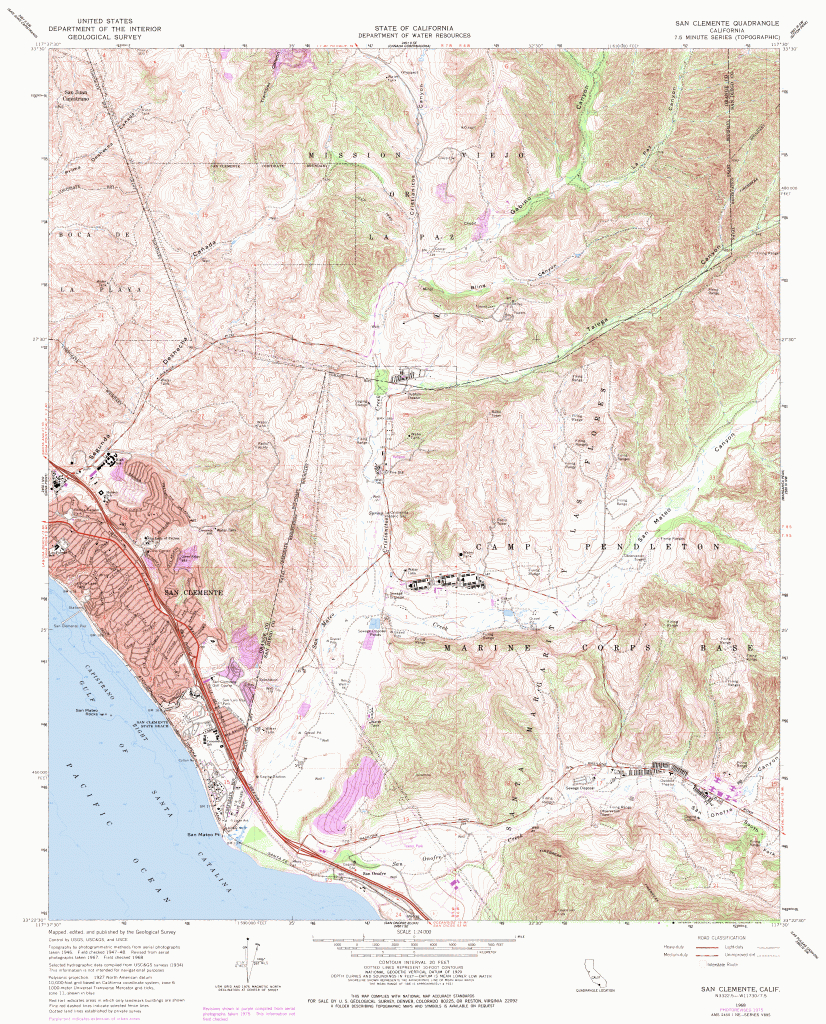
Delving into the Depths: Understanding Topographical Maps
A topographical map is not merely a flat representation of the Earth’s surface. It utilizes contour lines – lines connecting points of equal elevation – to depict the three-dimensional form of the terrain. These lines, like the rings of a tree trunk, provide a visual record of the gradual ascent and descent of the landscape, allowing us to perceive the subtle rises and falls of the land.
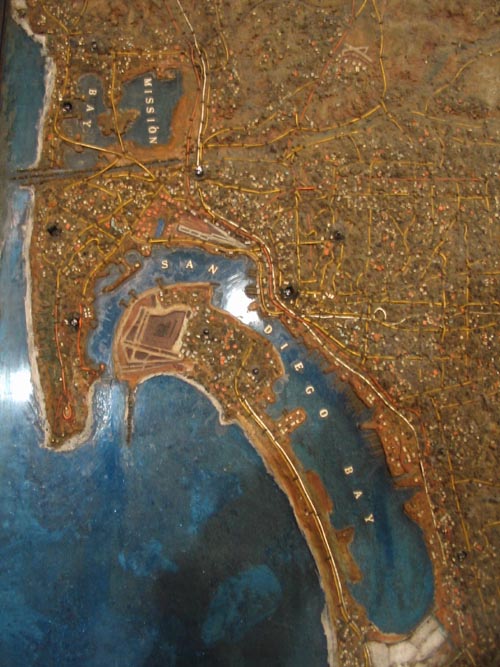
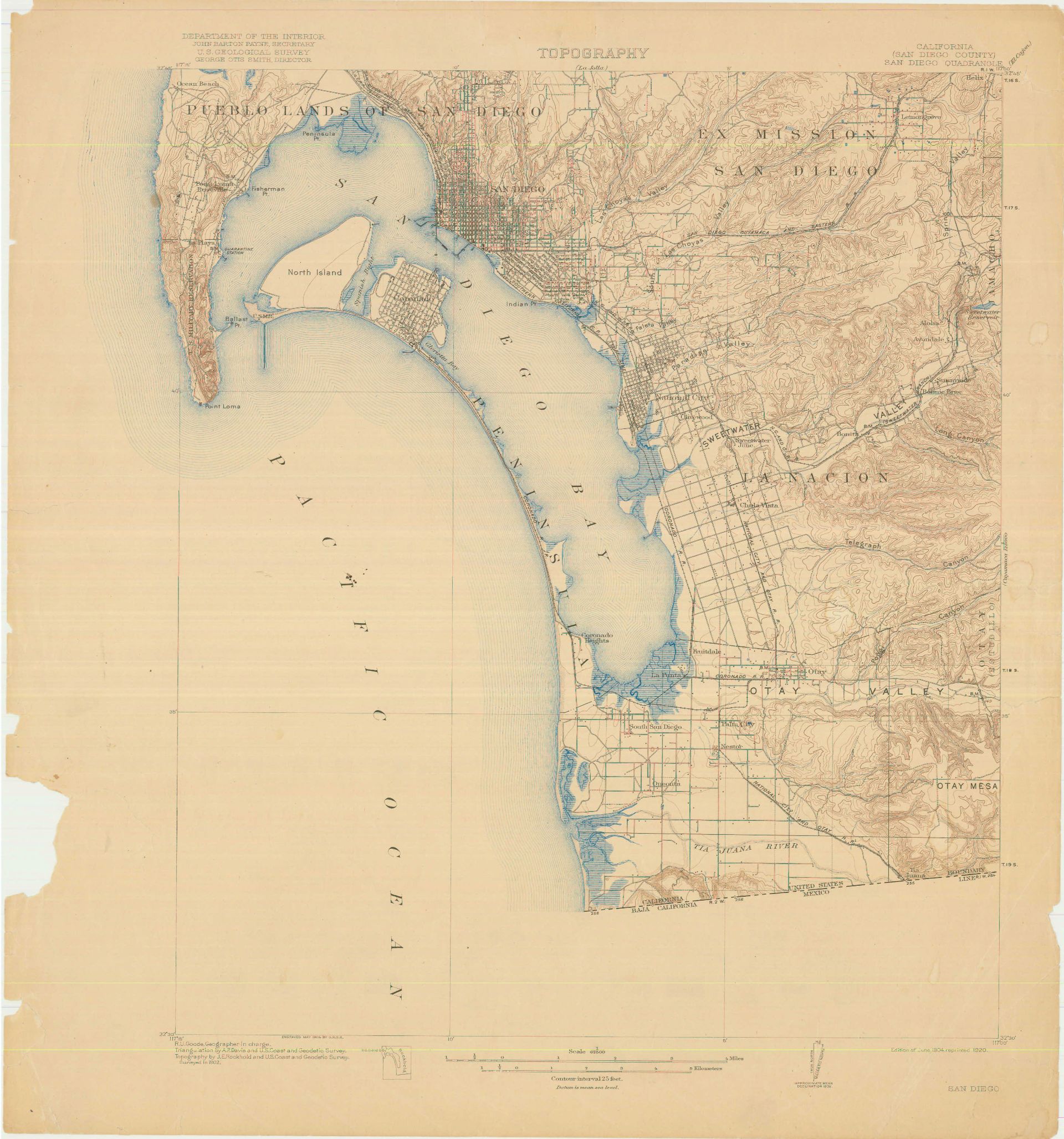
San Diego County’s Topographical Tapestry: A Detailed Overview
San Diego County’s topography is a testament to the region’s dynamic geological history, shaped by tectonic forces, erosion, and deposition. The map reveals a landscape characterized by:
-
Coastal Plains: The western edge of the county is dominated by a narrow coastal plain, a relatively flat expanse that stretches from the Pacific Ocean inland. This region, home to bustling cities like San Diego, offers a unique blend of urban development and natural beauty.
-
Peninsular Ranges: Rising dramatically from the coastal plain, the Peninsular Ranges form the backbone of the county. These mountains, a continuation of the Sierra Nevada, are characterized by their rugged terrain, steep slopes, and deep canyons. They are home to diverse ecosystems, including chaparral, forests, and grasslands, and serve as a vital watershed for the region.
-
The San Jacinto Mountains: As part of the Peninsular Ranges, the San Jacinto Mountains are a prominent feature in the eastern portion of the county. Their highest peak, San Jacinto Peak, reaches over 10,800 feet, offering breathtaking views and a challenging climb for experienced hikers.
-
The Santa Ana Mountains: A continuation of the Peninsular Ranges, the Santa Ana Mountains extend into the northern portion of the county. These mountains, characterized by their rugged terrain and diverse vegetation, provide a critical buffer against urban sprawl and offer a haven for wildlife.
-
The San Diego River: Flowing through the heart of the county, the San Diego River is a vital artery, providing water for agriculture, industry, and urban areas. Its meandering course through the landscape has shaped the surrounding topography, creating fertile valleys and floodplains.
The Importance of Topography: A Multifaceted Impact
The topographical map of San Diego County is not just a visual representation; it is a powerful tool that reveals the intricate relationships between the land and its inhabitants. Understanding this topography is crucial for:
-
Resource Management: The map provides valuable insights into the location of water resources, including groundwater aquifers, watersheds, and streams. This information is essential for managing water supply, mitigating drought, and protecting water quality.
-
Land Use Planning: The map allows planners to identify areas suitable for development, agriculture, recreation, and conservation. By understanding the terrain’s slope, elevation, and soil type, planners can make informed decisions about land use, minimizing environmental impact and promoting sustainable development.
-
Disaster Preparedness: The map helps identify areas at risk from natural disasters such as floods, wildfires, and earthquakes. This information is vital for developing effective disaster mitigation strategies, ensuring the safety of communities, and minimizing damage to infrastructure.
-
Environmental Conservation: The map reveals the distribution of diverse ecosystems, from coastal wetlands to mountain forests. This information is crucial for prioritizing conservation efforts, protecting endangered species, and maintaining biodiversity.
-
Recreation and Tourism: The map highlights the county’s recreational opportunities, from hiking trails in the mountains to beaches along the coast. By understanding the terrain, visitors can plan their adventures, explore hidden gems, and appreciate the beauty of the region.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the highest and lowest points in San Diego County?
A: The highest point in San Diego County is San Jacinto Peak, at 10,834 feet. The lowest point is sea level, along the Pacific Ocean coastline.
Q: How does the topography affect the climate of San Diego County?
A: San Diego County experiences a diverse range of climates due to its varied topography. The coastal areas enjoy mild temperatures and moderate rainfall, while the mountains experience colder winters and heavier snowfall. The rain shadow effect, caused by the Peninsular Ranges, results in drier conditions on the eastern side of the mountains.
Q: What are some of the significant geological features of San Diego County?
A: San Diego County is home to a variety of geological features, including the San Andreas Fault, which runs along the western edge of the county and is responsible for many earthquakes. The county also boasts numerous canyons, mesas, and valleys, formed by erosion and deposition over millions of years.
Tips for Navigating a Topographical Map
-
Familiarize Yourself with the Legend: The map’s legend explains the symbols and colors used to represent different features, such as elevation, water bodies, and vegetation.
-
Understand Contour Lines: Contour lines connect points of equal elevation. The closer the lines are together, the steeper the slope.
-
Use the Scale: The map’s scale indicates the ratio between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground. This information is crucial for accurately measuring distances and elevations.
-
Consider Your Purpose: The specific information you need from the map will determine how you interpret it. For example, if you are planning a hike, you will need to pay attention to elevation changes and trail routes.
Conclusion
The topographical map of San Diego County is a valuable resource for understanding the intricate relationships between the land, its inhabitants, and the environment. It reveals the region’s diverse ecosystems, its potential for development, and its vulnerability to natural disasters. By appreciating the nuances of the landscape, we can make informed decisions about land use, resource management, and conservation, ensuring the sustainable future of this vibrant and beautiful region.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Topographical Exploration of San Diego County. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
