Unveiling the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Scale
Related Articles: Unveiling the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Scale
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Scale. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Scale
Maps are powerful tools that allow us to navigate the world, understand spatial relationships, and visualize complex data. At the heart of every map lies a crucial element: scale. Map scale represents the relationship between distances on a map and the corresponding distances on the ground. Understanding this relationship is essential for accurate interpretation and effective use of maps.
Deciphering the Language of Scale
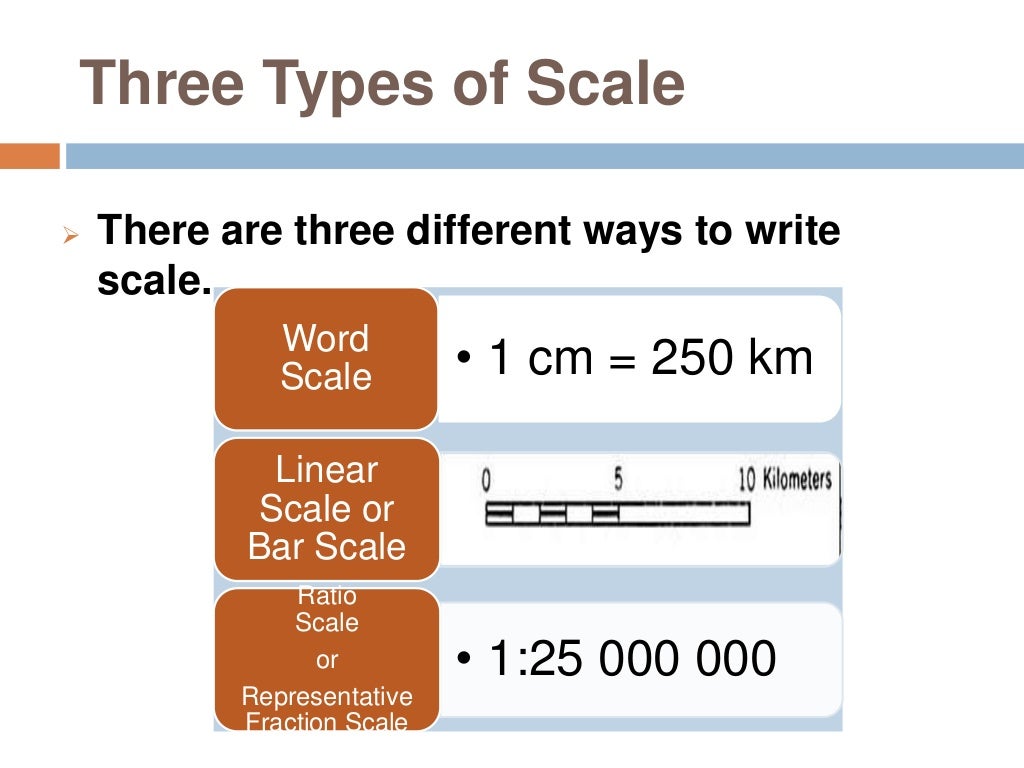
Map scale is expressed in various ways, each conveying the same fundamental concept: the ratio between map distance and real-world distance. The most common methods include:
1. Verbal Scale: This method states the relationship in words, such as "1 centimeter on the map represents 1 kilometer on the ground." This straightforward approach is easily understood but lacks the precision of other methods.
2. Representative Fraction (RF): Expressed as a fraction or ratio, RF represents the relationship between map distance and real-world distance. For example, 1:100,000 indicates that one unit on the map corresponds to 100,000 units on the ground. This method is widely used due to its clarity and consistency.
3. Graphic Scale: This method utilizes a visual representation of the scale using a bar or line. The bar is divided into segments representing specific distances on the ground, allowing for quick and easy estimation of real-world distances.
Understanding the Implications of Scale
The choice of map scale significantly impacts the level of detail and the extent of the area represented. A large-scale map, with a small RF (e.g., 1:10,000), depicts a smaller area with greater detail, suitable for local planning or navigation. Conversely, a small-scale map, with a large RF (e.g., 1:1,000,000), covers a vast area but with less detail, useful for regional or global perspectives.
Benefits of Understanding Map Scale
Comprehending map scale unlocks a world of possibilities:
- Accurate Distance Measurement: Map scale enables precise measurement of distances between points on the map, translating them into real-world distances.
- Effective Area Comparison: By comparing the sizes of different areas on a map, users can gain insights into relative proportions and spatial relationships.
- Data Interpretation: Scale influences the level of detail displayed on a map, enabling users to analyze data relevant to the chosen scale.
- Navigation and Orientation: Understanding map scale facilitates accurate navigation, allowing users to determine their location and plan routes efficiently.
- Spatial Analysis: Scale plays a crucial role in spatial analysis, enabling researchers to investigate patterns, trends, and relationships across different scales.
FAQs on Map Scale
1. How do I determine the scale of a map?
The scale of a map is typically indicated on the map itself, either verbally, as a representative fraction, or graphically.
2. What is the difference between a large-scale map and a small-scale map?
A large-scale map depicts a smaller area with greater detail, while a small-scale map covers a larger area with less detail.
3. Why is map scale important for navigation?
Map scale allows users to accurately measure distances and determine their location on a map, facilitating efficient navigation.
4. How does map scale affect data analysis?
The scale of a map determines the level of detail displayed, influencing the types of data and patterns that can be analyzed.
5. Can I change the scale of a map?
Maps can be scaled up or down using specialized software, but this can affect the accuracy and clarity of the data.
Tips for Effective Use of Map Scale
- Always check the scale of a map before using it.
- Use the appropriate scale for the task at hand.
- Be aware of the limitations of map scale.
- Practice measuring distances and calculating areas using map scale.
- Utilize online resources and tools for map scale conversion and calculations.
Conclusion
Map scale serves as the fundamental language of maps, enabling accurate interpretation and effective use of these valuable tools. Understanding the relationship between map distances and real-world distances is crucial for navigating, analyzing spatial data, and gaining insights from maps. By embracing the principles of map scale, users can unlock the full potential of these powerful visual representations of our world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Scale. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
