Unveiling the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scales and their Mathematical Foundation
Related Articles: Unveiling the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scales and their Mathematical Foundation
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scales and their Mathematical Foundation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scales and their Mathematical Foundation
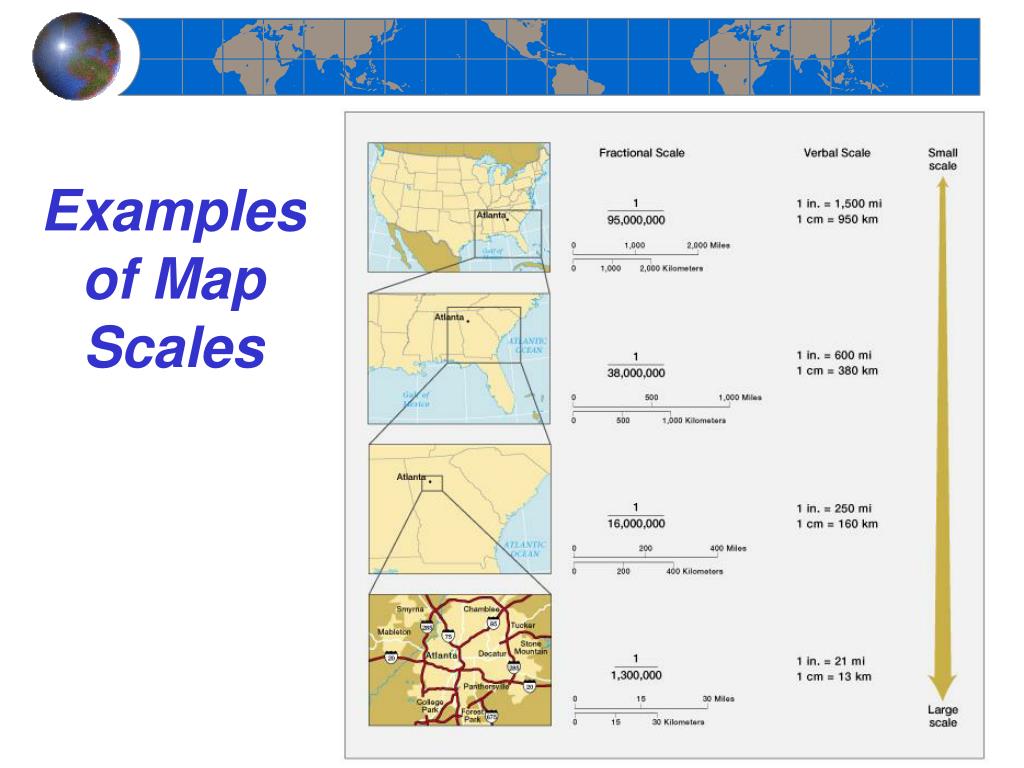
Maps are powerful tools, allowing us to navigate, explore, and understand the world around us. They are essentially scaled-down representations of reality, capturing the intricate details of landscapes, cities, and geographical features. The key to unlocking the information encoded within a map lies in comprehending its scale, the mathematical relationship between distances on the map and their corresponding distances in the real world.
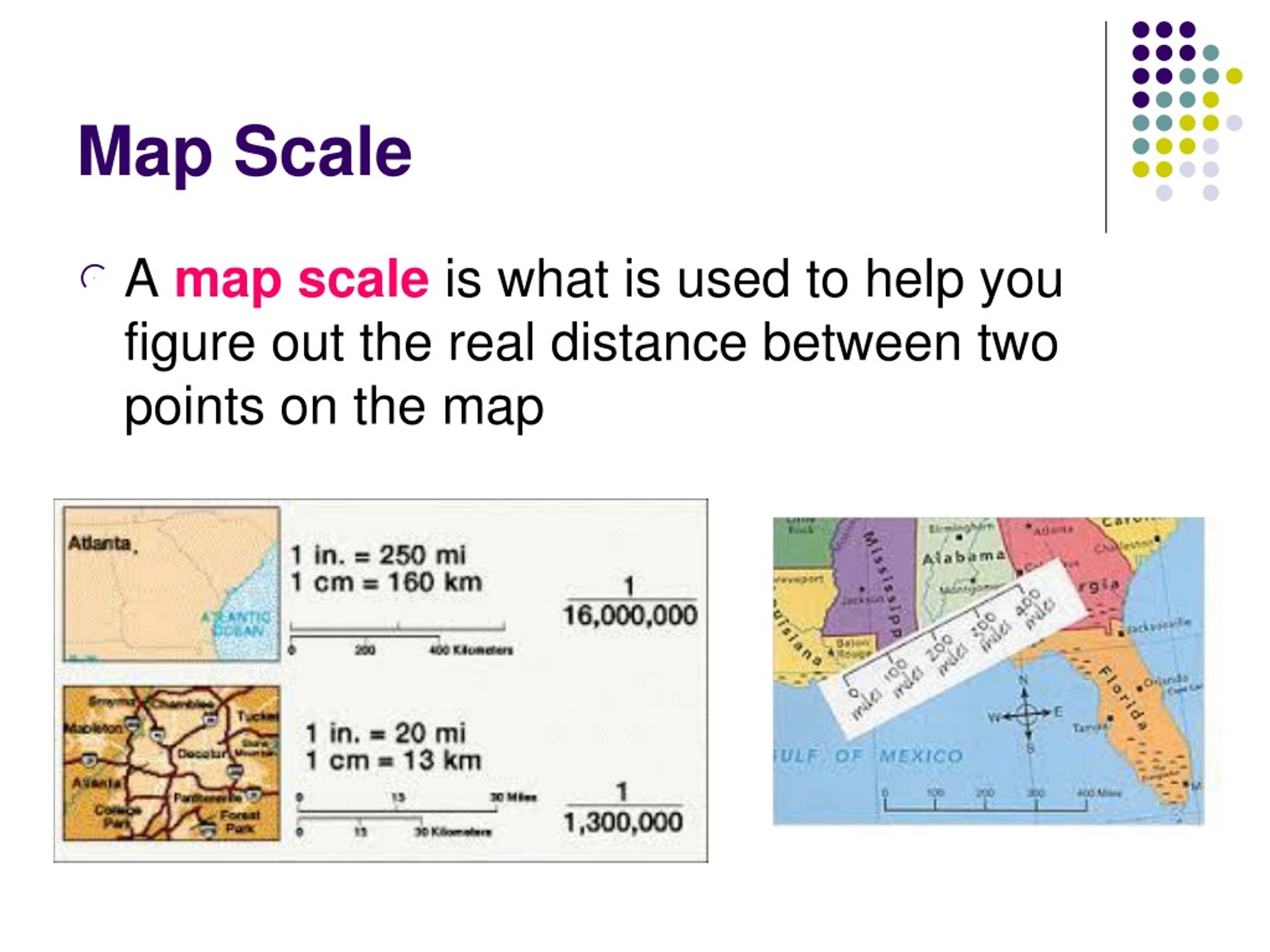
The Concept of Map Scale:
Map scale represents the ratio between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground. This ratio can be expressed in three primary ways:
1. Verbal Scale: This is the most straightforward representation, using words to describe the relationship. For example, a verbal scale of "1 centimeter to 10 kilometers" indicates that every centimeter on the map corresponds to 10 kilometers in reality.
2. Representative Fraction (RF): This is a numerical representation of the scale, expressed as a fraction or ratio. For example, an RF of 1:100,000 signifies that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units in the real world.
3. Graphic Scale: This is a visual representation of the scale, typically a line segment divided into smaller units representing specific distances on the ground. This allows for easy measurement directly on the map.
The Importance of Map Scales:
Understanding map scales is paramount for several reasons:
-
Accurate Distance Measurement: Map scales enable precise distance calculations between locations on the map, allowing for accurate route planning, travel estimations, and land area calculations.
-
Interpretation of Spatial Relationships: By comprehending the scale, one can accurately interpret the relative sizes and positions of features on the map, gaining a deeper understanding of the geographic relationships between them.
-
Data Analysis and Interpretation: Map scales are crucial for analyzing and interpreting data presented on maps, such as population density, land use patterns, and environmental indicators.
Mathematical Operations with Map Scales:
The mathematical foundation of map scales allows for various calculations:
-
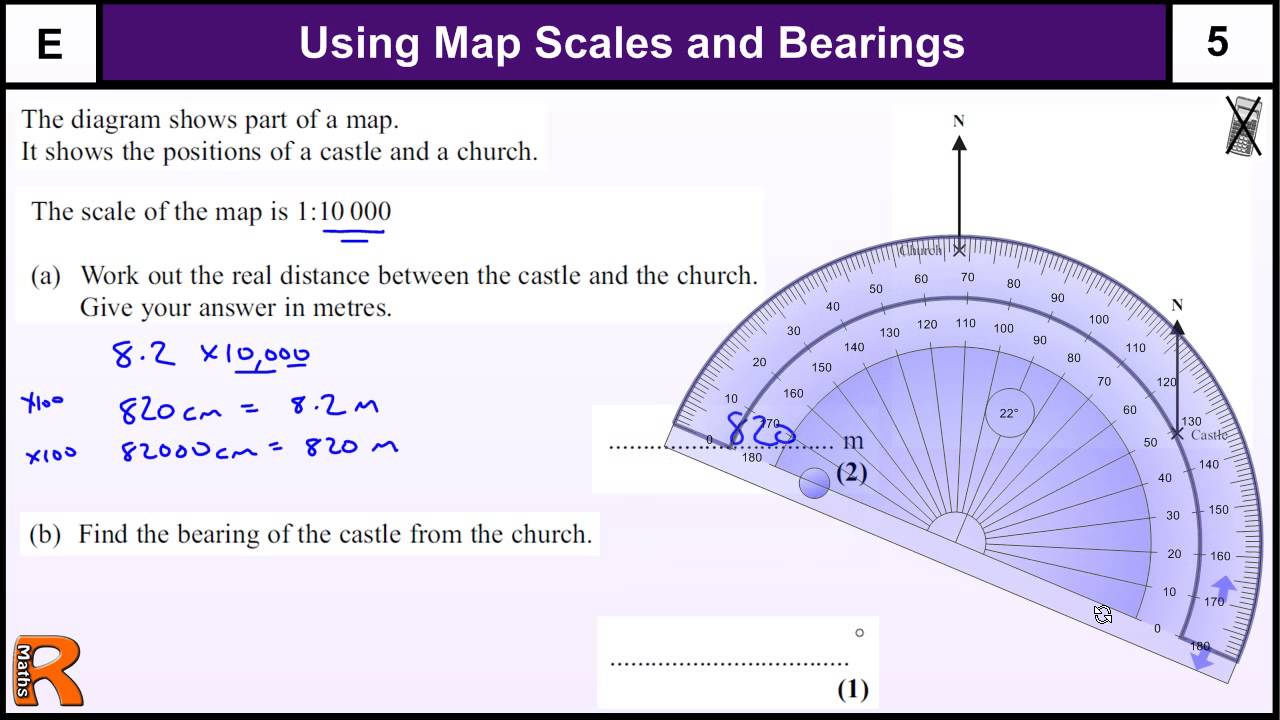
Converting Map Distances to Real-World Distances: To convert a distance measured on the map to the actual distance, multiply the map distance by the scale factor. For example, if the map distance is 5 centimeters and the scale is 1:50,000, the real-world distance is 5 cm * 50,000 = 250,000 cm or 2.5 kilometers.
-
Converting Real-World Distances to Map Distances: To convert a real-world distance to a map distance, divide the real-world distance by the scale factor. For example, if the real-world distance is 10 kilometers (1,000,000 cm) and the scale is 1:50,000, the map distance is 1,000,000 cm / 50,000 = 20 cm.
-
Calculating Areas: To calculate the area of a feature on the map, first determine the area in square units (e.g., square centimeters) on the map. Then, multiply this area by the square of the scale factor to obtain the real-world area. For example, if the area on the map is 10 square centimeters and the scale is 1:50,000, the real-world area is 10 cm² * (50,000)² = 25,000,000,000 square centimeters or 25 square kilometers.
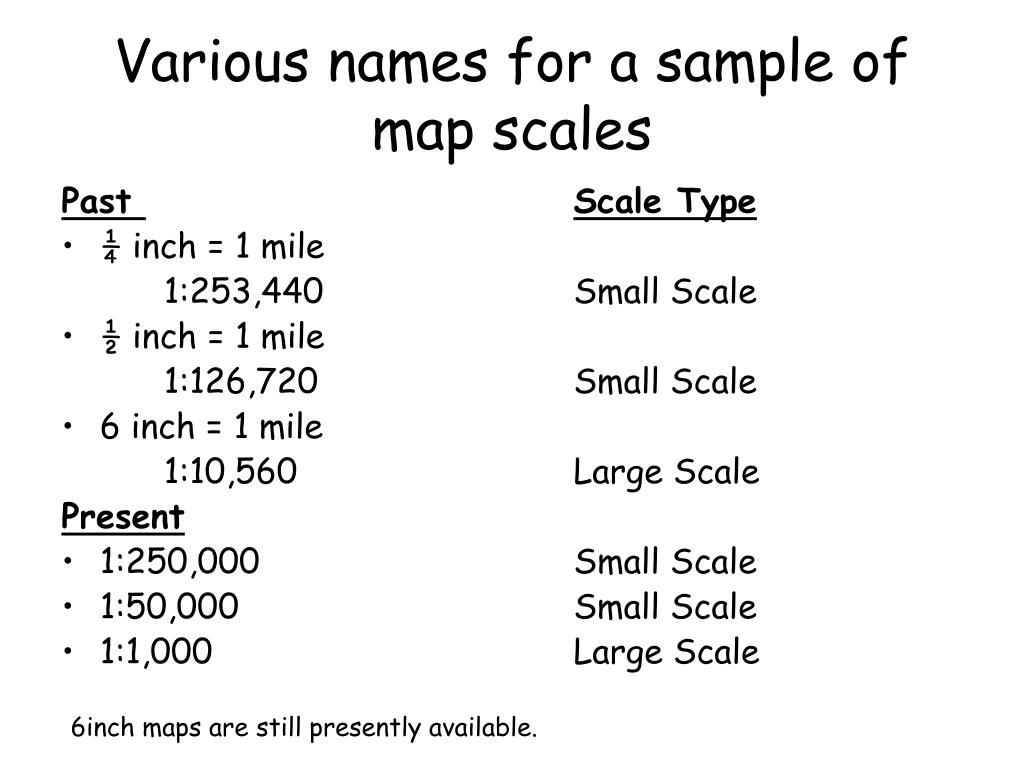
Types of Map Scales:
Map scales can be categorized into two primary types:
-
Large-Scale Maps: These maps depict a small area in detail, with a large scale factor (e.g., 1:10,000). They are commonly used for urban planning, engineering projects, and detailed land surveys.
-
Small-Scale Maps: These maps depict a large area with less detail, with a small scale factor (e.g., 1:10,000,000). They are typically used for world maps, regional maps, and general geographical overview.
Factors Influencing Map Scale Selection:
The choice of map scale depends on several factors, including:
-
Purpose of the Map: The intended use of the map dictates the level of detail required, influencing the scale selection.
-
Area of Coverage: The size of the area being mapped determines the scale factor needed to represent the features effectively.
-
Available Data: The availability and resolution of data sources influence the level of detail that can be accurately depicted on the map.
-
Technical Limitations: Printing and display capabilities can limit the scale of a map, particularly for large-scale maps with intricate details.
Challenges and Considerations:
While map scales provide a powerful tool for representing geographical information, certain challenges and considerations arise:
-
Distortion: Map projections, used to represent the curved Earth on a flat surface, inevitably introduce distortions in shape, size, and distance. These distortions become more pronounced at smaller scales.
-
Generalization: Due to limitations in space and detail, maps require generalization, where smaller features are omitted or combined to represent the larger patterns. This can lead to inaccuracies or misinterpretations, especially at smaller scales.
-
Scale Variation: Some maps may have varying scales across different parts of the map, making accurate measurements more challenging.
FAQs on Map Scales:
1. What is the difference between a large-scale map and a small-scale map?
A large-scale map depicts a smaller area with greater detail, while a small-scale map shows a larger area with less detail. The scale factor is larger for large-scale maps and smaller for small-scale maps.
2. How do I determine the scale of a map?
The scale is typically indicated on the map itself, either verbally, as a representative fraction, or graphically. If not explicitly stated, you can determine the scale by measuring a known distance on the map and comparing it to the corresponding real-world distance.
3. What is the significance of map scale in cartography?
Map scale is fundamental in cartography as it determines the level of detail and accuracy of the map representation. It allows for precise distance measurements, accurate interpretation of spatial relationships, and effective data analysis.
4. How does map scale affect the perception of geographical features?
The scale of a map influences the perception of features by determining the level of detail and the relative sizes and positions of objects. Large-scale maps emphasize local details, while small-scale maps focus on broader patterns and regional relationships.
5. What are the limitations of map scales?
Map scales are subject to limitations due to distortions introduced by map projections, generalization of features, and potential variations in scale across the map. These limitations can affect the accuracy and interpretation of map information.
Tips for Using Map Scales Effectively:
-
Pay close attention to the scale indicated on the map.
-
Use the scale to calculate distances and areas accurately.
-
Be aware of the limitations of map scales, particularly distortions and generalization.
-
Consider the purpose of the map and choose a scale appropriate for the intended use.
-
Compare different maps with varying scales to gain a comprehensive understanding of the area.
Conclusion:
Map scales serve as the language of maps, enabling us to understand and interpret the information encoded within them. By comprehending the mathematical relationship between distances on the map and the real world, we can accurately measure distances, analyze spatial relationships, and interpret data presented on maps. Understanding map scales is essential for navigation, exploration, and gaining a deeper understanding of the world around us.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scales and their Mathematical Foundation. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
