Unveiling the Power of Map Scale: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Geographic Data
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Map Scale: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Geographic Data
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Map Scale: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Geographic Data. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Map Scale: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Geographic Data
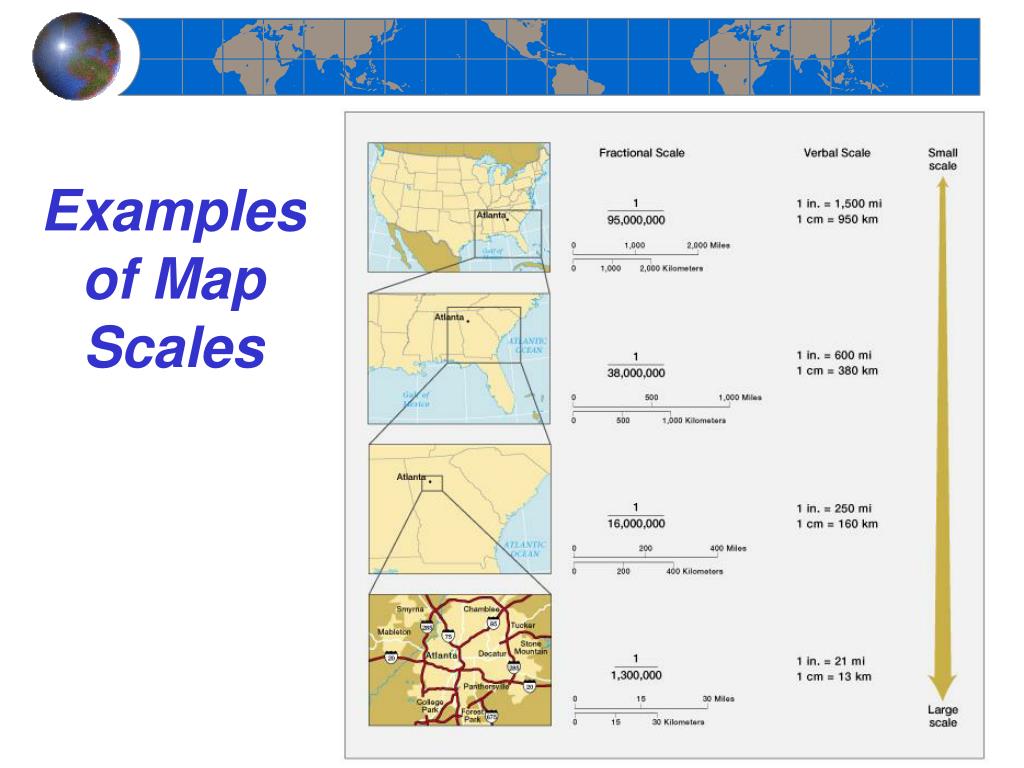
Maps are powerful tools for understanding and navigating the world around us. They condense vast landscapes into manageable representations, enabling us to comprehend spatial relationships and visualize geographical phenomena. However, the accuracy and clarity of a map hinge on one crucial element: scale.
Map scale, a fundamental concept in cartography, defines the relationship between the distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. It essentially dictates how much the real world is compressed or shrunk to fit onto a map. This seemingly simple concept holds immense power, influencing the level of detail, the intended use, and the overall effectiveness of any map.
Understanding the Essence of Map Scale
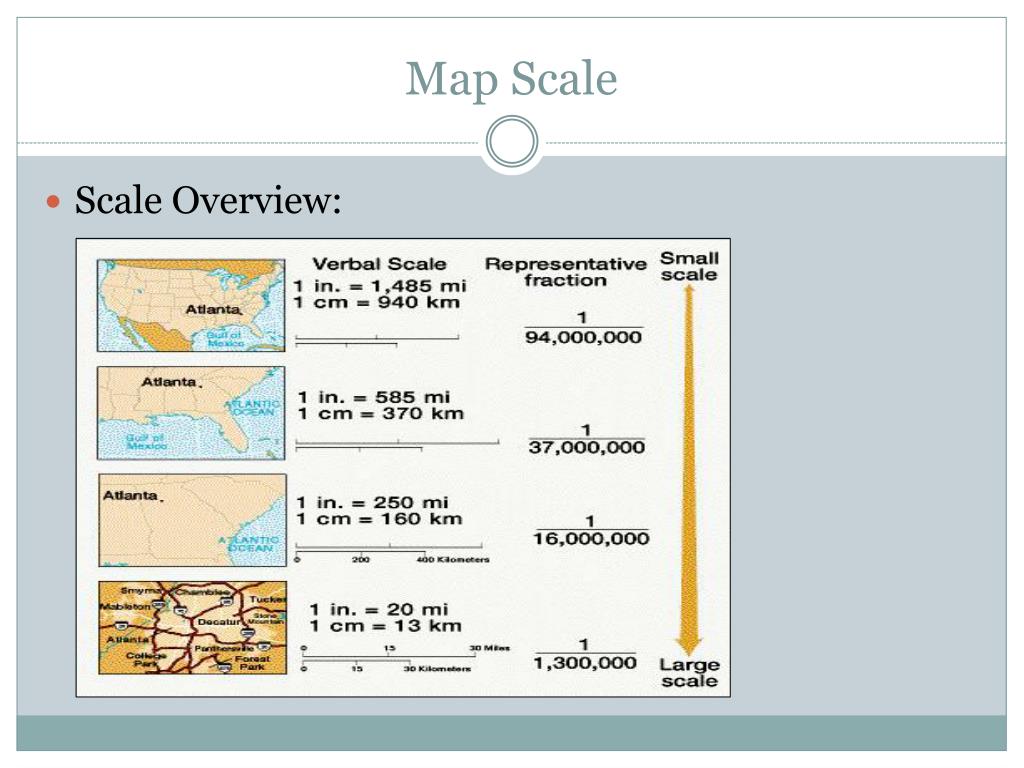
Map scale is typically represented in three primary ways:
1. Verbal Scale: This method expresses the relationship between map distance and ground distance in words. For instance, a verbal scale of "1 centimeter represents 10 kilometers" indicates that every centimeter on the map corresponds to 10 kilometers in reality.
2. Representative Fraction (RF): This numerical approach presents the scale as a fraction, where the numerator represents the map distance and the denominator represents the corresponding ground distance. For example, an RF of 1:100,000 signifies that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units on the ground.
3. Graphic Scale: This visual representation utilizes a line segment divided into units that correspond to specific distances on the ground. A graphic scale allows for direct measurement of distances on the map and their translation to real-world distances.
The Significance of Map Scale in Cartography
Map scale is not merely a technical detail; it is a critical element that dictates the map’s purpose and usefulness. It determines:
-
Level of Detail: A large-scale map, with a smaller RF, depicts a smaller area with a higher level of detail. This is ideal for maps focusing on specific localities, urban areas, or intricate features. Conversely, a small-scale map, with a larger RF, encompasses a larger area but sacrifices detail, making it suitable for depicting global patterns, continental landscapes, or broad geographical trends.
-
Intended Use: The choice of scale depends on the intended use of the map. Navigational maps, requiring precise location information, often utilize large scales to highlight local features and facilitate accurate route planning. Conversely, thematic maps, designed to showcase patterns and distributions, may employ smaller scales to provide a broader perspective on geographical phenomena.
-
Map Accuracy: Scale plays a vital role in map accuracy. A large-scale map, with its finer detail, offers greater precision for measuring distances and identifying specific locations. Conversely, a small-scale map, while covering a larger area, sacrifices accuracy in depicting minute details.
The Impact of Scale on Map Interpretation
Understanding map scale is crucial for accurate interpretation of mapped information. Misinterpreting scale can lead to misjudging distances, sizes, and the relative significance of features. For instance, a small-scale map might make a small city appear larger than a much larger city on a large-scale map, simply due to the difference in scale.
Using Map Scale Effectively
To effectively utilize map scale, cartographers and map users must consider:
-
Choosing the Appropriate Scale: The choice of scale depends on the map’s purpose and intended audience. A map designed for navigation should employ a large scale to ensure accuracy, while a map showcasing global trends would benefit from a smaller scale to provide a broader perspective.
-
Utilizing Scale Bars: Graphic scales, commonly known as scale bars, are essential for converting distances on the map to real-world distances. They provide a visual reference point for direct measurement and understanding of the map’s scale.
-
Understanding Scale Distortion: All maps, especially those depicting large areas, inevitably experience some degree of distortion. This is because the Earth’s curved surface is projected onto a flat map, resulting in variations in shape, size, and distance. Understanding scale distortion is crucial for accurate map interpretation.
FAQs on Map Scale
Q: What is the difference between a large-scale map and a small-scale map?
A: A large-scale map depicts a smaller area with greater detail, while a small-scale map covers a larger area with less detail.
Q: How can I determine the scale of a map?
A: The scale of a map can be determined by examining its verbal scale, representative fraction (RF), or graphic scale.
Q: Why is map scale important for navigation?
A: Map scale is crucial for navigation because it determines the accuracy of distance measurements and the level of detail required for route planning.
Q: What are some examples of how scale impacts map interpretation?
A: A small-scale map might make a small city appear larger than a larger city on a large-scale map, due to the difference in scale. Similarly, a map with a smaller scale might exaggerate the size of a mountain range compared to its actual size.
Tips for Utilizing Map Scale Effectively
-
Always pay attention to the map’s scale. This will help you understand the relationship between the map and the real world.
-
Use a scale bar to measure distances on the map. This allows for accurate conversion of map distances to real-world distances.
-
Be aware of scale distortion. Remember that all maps, especially those depicting large areas, experience some degree of distortion.
-
Choose the appropriate scale for your needs. Consider the purpose of the map and the level of detail required.
Conclusion
Map scale is a fundamental concept in cartography, influencing the accuracy, detail, and overall effectiveness of any map. Understanding map scale is crucial for accurate interpretation of mapped information, making informed decisions, and utilizing maps effectively for navigation, analysis, and visualization of geographical data. By mastering the concept of map scale, we gain a deeper appreciation for the power of maps as tools for understanding and interacting with the world around us.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Map Scale: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Geographic Data. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
