Unveiling the Power of Map Scales: Understanding Distance on Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Map Scales: Understanding Distance on Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Map Scales: Understanding Distance on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Map Scales: Understanding Distance on Maps
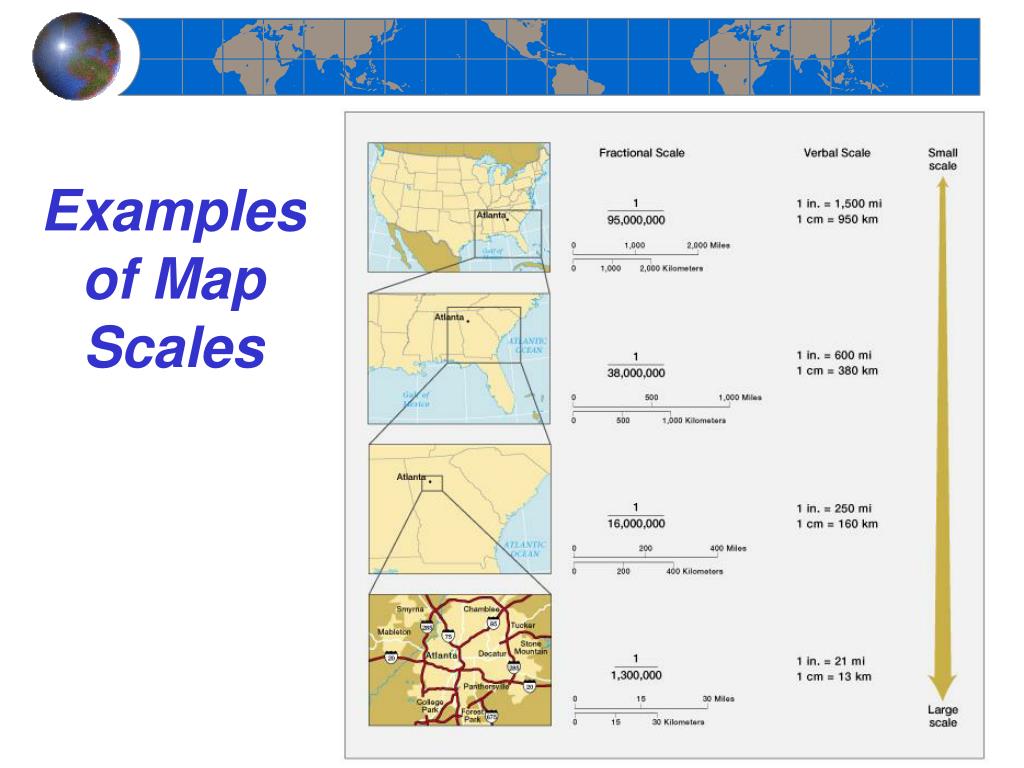
Maps are invaluable tools for navigating the world, providing a visual representation of our surroundings. However, their true utility hinges on understanding the concept of map scale – the crucial element that translates distances on the map to real-world distances. This article delves into the intricacies of map scales, focusing on those that express distance in miles, and explores their importance in various applications.
The Essence of Map Scales
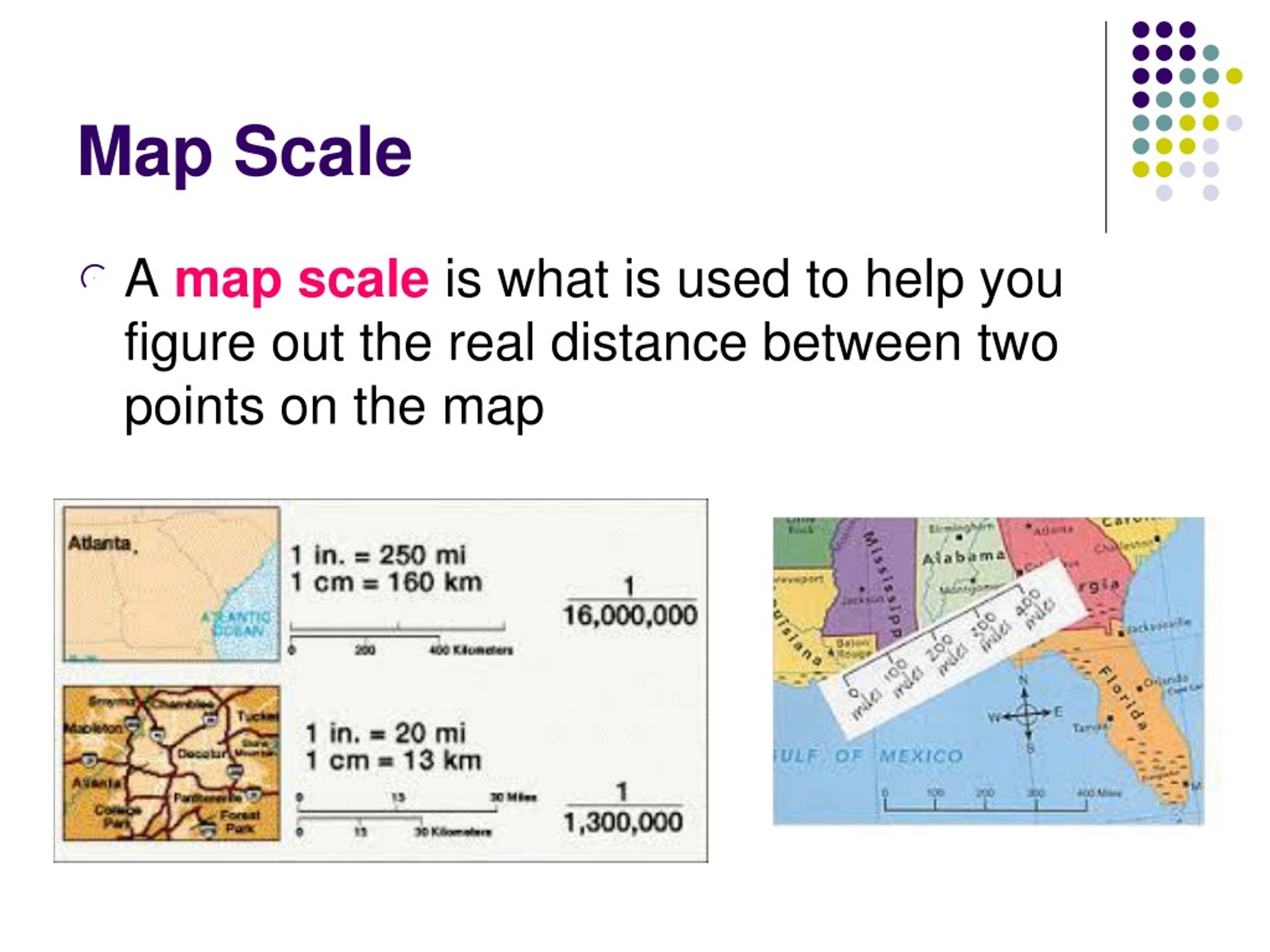
A map scale acts as a bridge between the miniature world depicted on a map and the vast expanse of reality. It establishes a precise relationship between distances measured on the map and their corresponding distances on the ground. This relationship is crucial for accurate interpretation and application of map information.
Understanding Map Scales in Miles
Map scales expressing distance in miles are commonly found in maps designed for travel, exploration, and general geographical understanding. They typically present the ratio between map distance and real-world distance in a straightforward manner. For instance, a map scale of "1 inch = 10 miles" indicates that every inch measured on the map represents 10 miles on the ground.
Types of Map Scales
Map scales are presented in various formats, each offering a unique approach to representing distance:
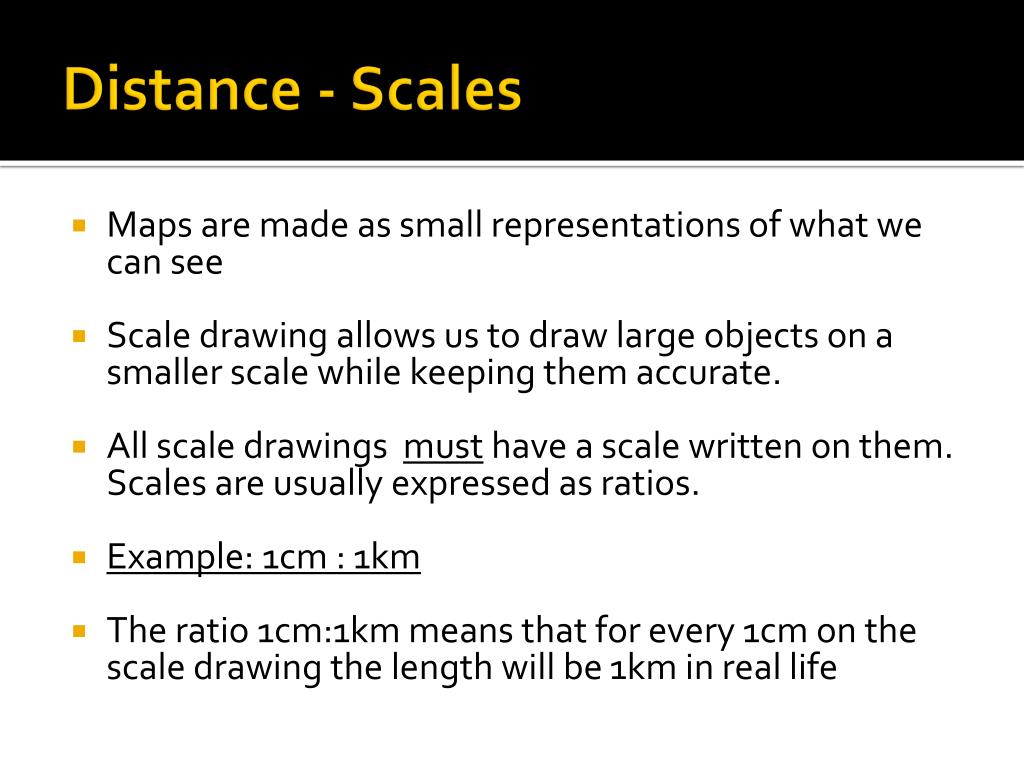
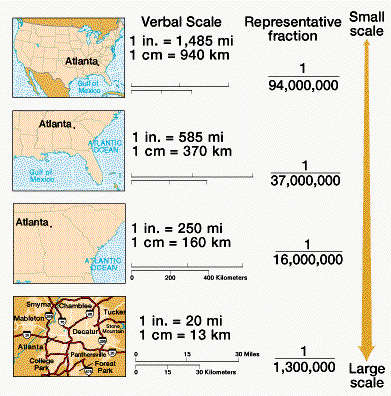
- Verbal Scale: This straightforward method explicitly states the relationship between map distance and real-world distance, for example, "1 inch = 10 miles."
- Representative Fraction (RF): Expressed as a ratio, the RF represents the map distance as a fraction of the real-world distance. A scale of 1:100,000 implies that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units on the ground.
- Graphic Scale: A visual representation of the scale, usually depicted as a line divided into segments representing specific distances. This allows for direct measurement of distances on the map without relying on calculations.
The Significance of Map Scales
The accuracy and usefulness of maps hinge on the proper interpretation and application of map scales. They empower us to:
- Measure Distances: Precisely determine the distances between locations on the map, crucial for planning journeys, estimating travel time, and understanding geographical relationships.
- Calculate Areas: Determine the size of land parcels, geographical features, or regions by converting map measurements into real-world dimensions.
- Compare Sizes: Effectively evaluate the relative sizes of different locations, features, or regions depicted on the map.
- Visualize Geographic Relationships: Gain a comprehensive understanding of the spatial relationships between locations, features, and regions, facilitating informed decision-making in various fields.
Applications of Map Scales in Miles
Map scales play a pivotal role in diverse fields, enabling accurate analysis and informed decision-making:
- Navigation: Essential for travelers, drivers, and hikers, allowing them to plan routes, calculate travel times, and navigate unfamiliar territories.
- Urban Planning: Used to analyze urban sprawl, assess infrastructure needs, and plan efficient land use, contributing to sustainable city development.
- Environmental Studies: Enable the mapping and analysis of natural resources, environmental hazards, and ecological patterns, supporting conservation efforts and environmental management.
- Military Operations: Critical for planning military maneuvers, deploying troops, and coordinating logistics, ensuring strategic advantage in tactical scenarios.
- Disaster Response: Used to assess the extent of damage, plan relief efforts, and manage resources during natural disasters, ensuring effective and timely response.
Factors Affecting Map Scale Choice
The choice of map scale depends on several factors, including:
- Purpose of the Map: The intended use dictates the level of detail required, influencing the scale. Maps for navigation typically use larger scales to show more detail, while maps for regional planning may use smaller scales to cover a broader area.
- Area Covered: The extent of the area depicted on the map influences the scale. Maps covering large regions require smaller scales to encompass the entire area, while maps focusing on specific locations may use larger scales for greater detail.
- Available Data: The availability of accurate data for specific regions and features influences the scale choice. Detailed data allows for larger scales, while limited data may necessitate smaller scales.
FAQs about Map Scales
Q: What is the difference between a large scale map and a small scale map?
A: A large scale map depicts a smaller area with more detail, while a small scale map covers a larger area with less detail. The numerical value of the scale is inversely proportional to the map’s scale. A larger scale map will have a smaller numerical value, while a smaller scale map will have a larger numerical value.
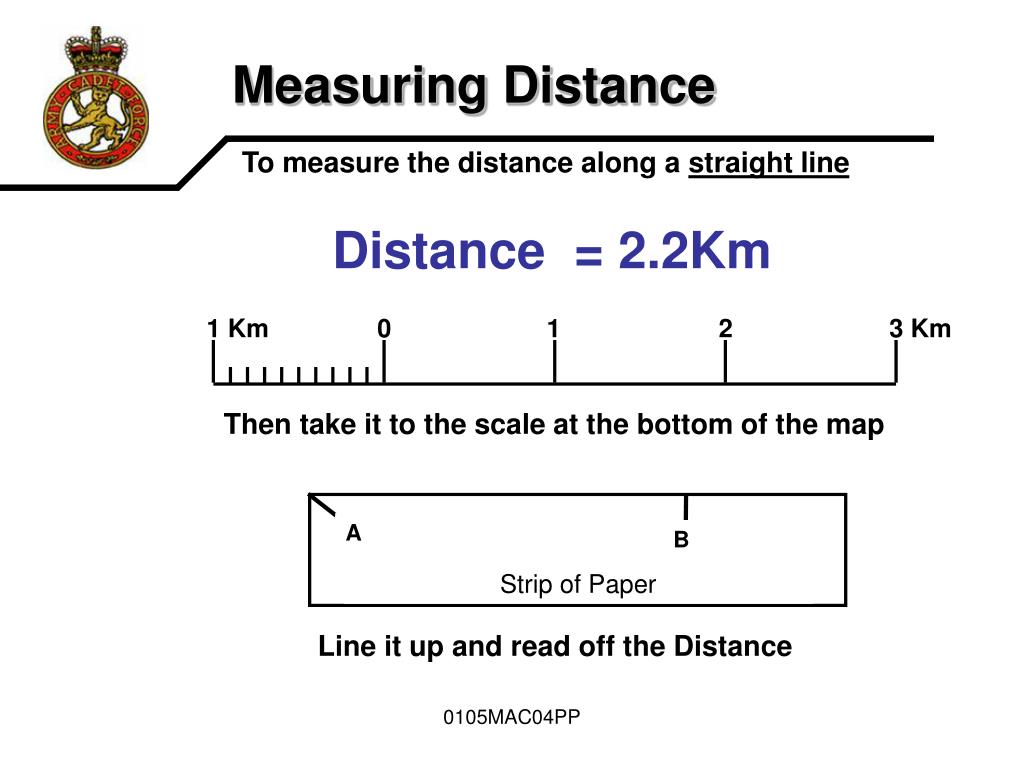
Q: How do I determine the distance between two points on a map?
A: Use a ruler to measure the distance between the two points on the map. Then, apply the map scale to convert the measured distance into real-world distance. For example, if the distance on the map is 2 inches and the scale is 1 inch = 10 miles, the real-world distance is 20 miles.
Q: Can I use a map scale from one map to another?
A: No. Different maps have different scales, so using a scale from one map to measure distances on another is inaccurate. Each map should be interpreted using its own specific scale.
Q: How do I create a map scale for a specific area?
A: To create a map scale for a specific area, you need to determine the desired level of detail and the area you want to represent. You can then use a variety of methods, including the verbal scale, representative fraction, or graphic scale, to express the relationship between map distance and real-world distance.
Tips for Using Map Scales
- Always refer to the map scale: Ensure you are using the correct scale for the map you are working with.
- Understand the units of measurement: Be aware of the units used in the map scale (e.g., miles, kilometers) and ensure consistency in your calculations.
- Use a ruler for accurate measurements: Measure distances on the map using a ruler or measuring tape for precise calculations.
- Pay attention to the type of scale: Understand the different types of map scales and their corresponding methods of interpreting distances.
- Practice interpreting scales: Regularly engage with maps and practice converting map distances to real-world distances to improve your understanding and accuracy.
Conclusion
Map scales are fundamental to the accurate interpretation and application of maps. They act as the bridge between the miniature world of maps and the vast reality we inhabit. Understanding map scales, particularly those expressing distance in miles, empowers us to measure distances, calculate areas, compare sizes, and visualize geographic relationships, enabling informed decision-making in various fields. By mastering the art of interpreting map scales, we unlock the full potential of these invaluable tools, enhancing our understanding of the world and guiding our interactions with it.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Map Scales: Understanding Distance on Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!

