Unveiling the Power of Overlapping Radius Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Overlapping Radius Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Overlapping Radius Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Overlapping Radius Maps: A Comprehensive Guide

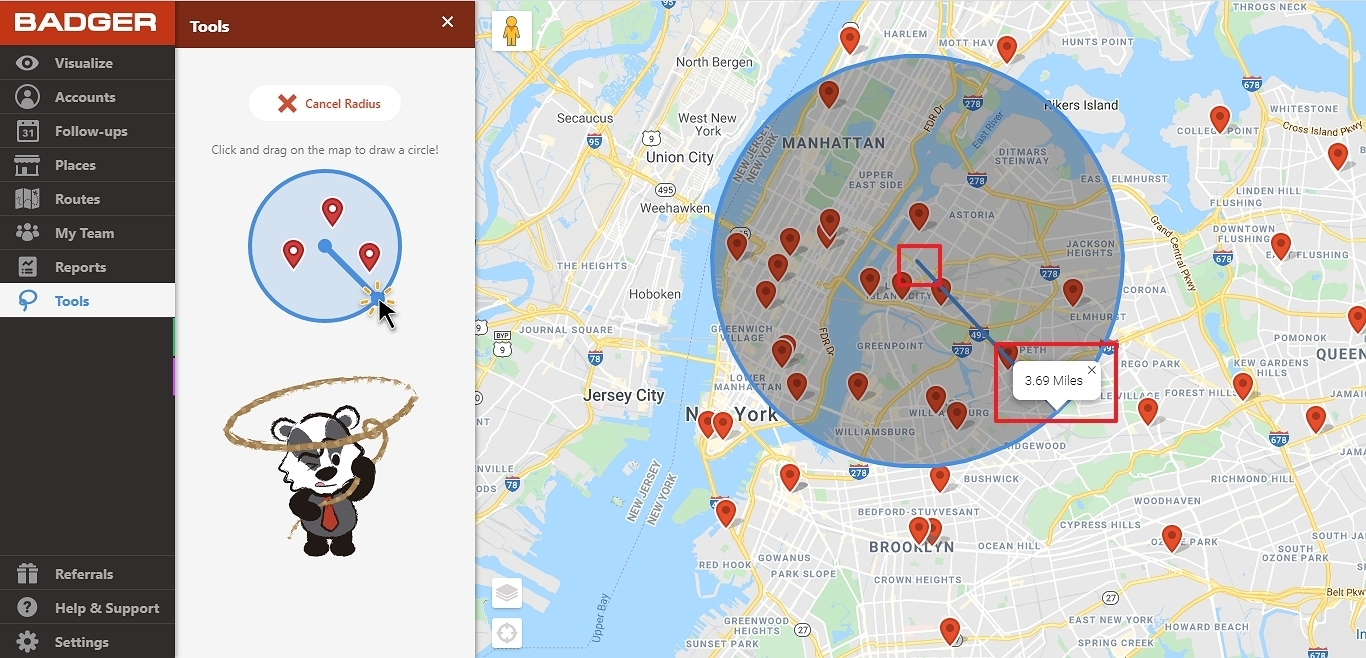
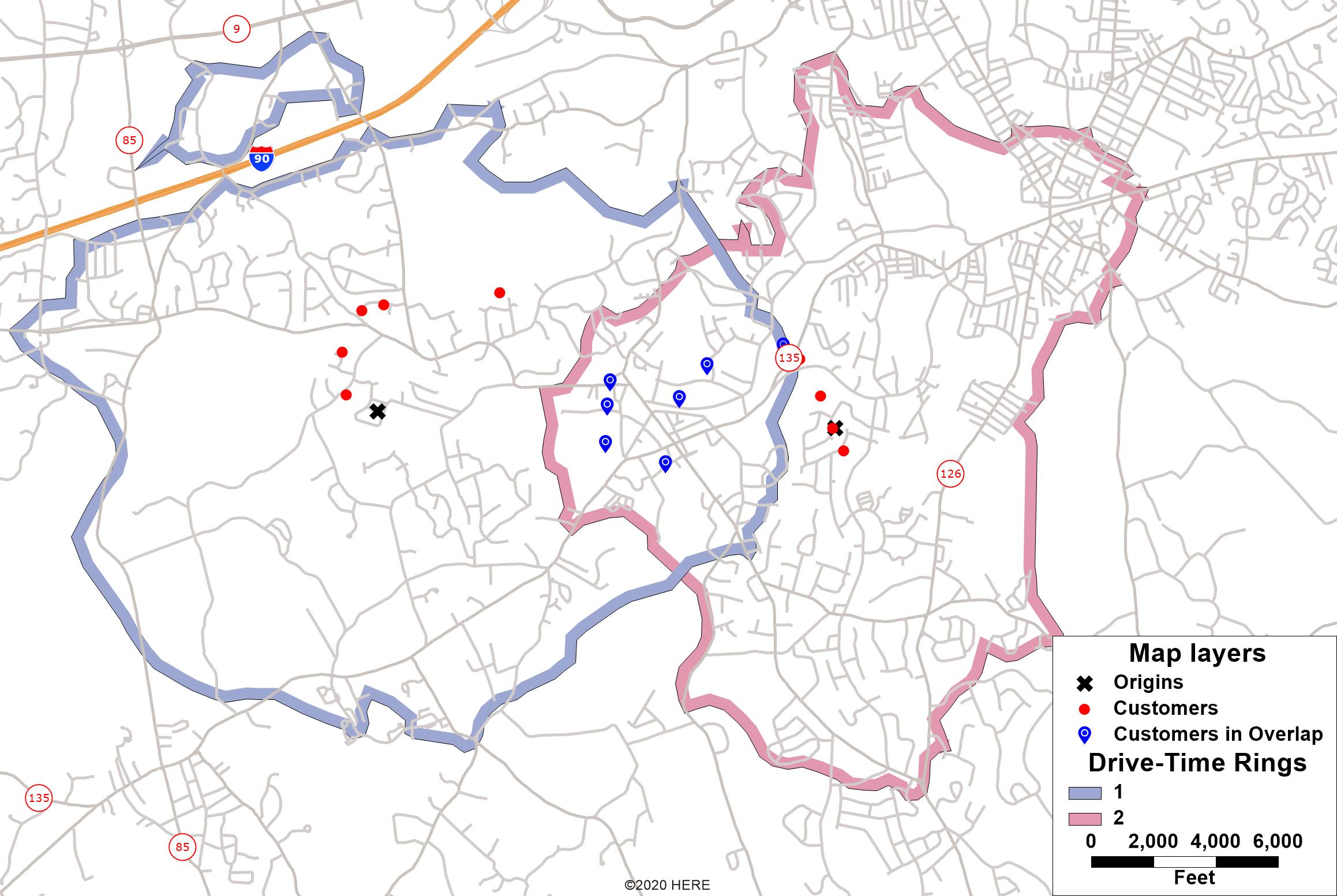
The realm of spatial analysis often necessitates visualizing and understanding the relationships between geographical entities. While traditional maps provide a static representation of locations, the concept of "overlapping radius maps" empowers a deeper understanding of spatial interactions and proximity. This technique, often employed in various fields including urban planning, market research, and public health, utilizes circular areas of influence to depict the interconnectedness of points within a geographic space.
Understanding the Fundamentals
At its core, an overlapping radius map is a visual representation where circles, each representing a point of interest, are drawn with radii that extend outwards to denote their influence or reach. The key element that distinguishes this technique lies in the overlap of these circles. When circles intersect, they highlight areas where the influence of multiple points converges, revealing areas of potential interaction, competition, or collaboration.
Beyond Simple Proximity: The Significance of Overlap
The true power of overlapping radius maps lies in their ability to transcend simple proximity analysis. While traditional distance-based maps may indicate the closest points, overlapping radius maps reveal the areas where multiple influences intersect, offering a richer understanding of spatial relationships. This is particularly valuable in scenarios where:
- Competition and Market Analysis: Businesses can analyze their market share and potential competition by visualizing the overlap between their service areas and those of their rivals.
- Service Provision and Accessibility: Healthcare providers, emergency services, and public transportation systems can utilize overlapping radius maps to assess service coverage, identify potential gaps, and optimize resource allocation.
- Urban Planning and Development: Planners can analyze the influence of amenities, infrastructure, and population density to guide decisions regarding zoning, transportation networks, and community development.
- Public Health and Disease Surveillance: Epidemiologists can visualize the spread of diseases, identify high-risk areas, and prioritize intervention strategies based on the overlap of potential exposure zones.
Visualizing the Intricacies of Spatial Relationships
The visual nature of overlapping radius maps allows for a clear and intuitive understanding of spatial relationships. By adjusting the radius of each circle, users can represent factors such as:
- Service Range: The radius can represent the maximum distance a service can be accessed or delivered.
- Influence Area: The radius can denote the area within which a specific point exerts its influence, be it a business, a school, or a public amenity.
- Probability of Interaction: The radius can represent the likelihood of interaction between two points based on factors such as distance, travel time, or service availability.
Beyond Static Visualization: The Dynamic Potential
The power of overlapping radius maps extends beyond static visualization. Through dynamic mapping tools, users can:
- Adjust radii interactively: Users can modify the radius of individual circles to explore different scenarios and analyze the impact of changing parameters.
- Layer multiple datasets: Combining overlapping radius maps with other geographic data layers, such as population density, income levels, or crime rates, provides a more comprehensive understanding of the spatial context.
- Analyze temporal trends: By incorporating time-series data, users can visualize the evolution of spatial relationships over time, revealing patterns of growth, decline, or change.
Unveiling the Hidden Insights: Applications in Diverse Fields
The versatility of overlapping radius maps has led to their adoption across diverse fields, each leveraging the technique to address specific challenges and uncover valuable insights.
- Retail and Marketing: Identifying ideal locations for new stores, analyzing customer catchment areas, and optimizing advertising campaigns based on the overlap of customer demographics and service areas.
- Transportation and Logistics: Optimizing delivery routes, identifying high-traffic areas, and evaluating the impact of infrastructure projects on transportation networks.
- Environmental Management: Analyzing the impact of pollution sources, identifying areas at risk from natural disasters, and optimizing resource allocation for conservation efforts.
- Education and Social Services: Understanding the accessibility of schools and social services, identifying underserved communities, and optimizing resource allocation for educational programs and social support initiatives.
FAQs on Overlapping Radius Maps
1. What are the key limitations of overlapping radius maps?
While powerful, overlapping radius maps have limitations:
- Oversimplification of reality: They represent a simplified view of spatial relationships, potentially neglecting factors like road networks, terrain, and individual preferences.
- Assumes uniform influence: They assume that influence is uniform within the radius, neglecting variations within the area.
- Limited by data availability: Accuracy depends on the quality and completeness of available data.
2. How can I create an overlapping radius map?
There are various tools available for creating overlapping radius maps, ranging from basic mapping software to specialized GIS platforms. Popular options include:
- Google Maps: Offers basic tools for drawing circles and analyzing proximity.
- ArcGIS: A powerful GIS software that provides advanced tools for creating and analyzing overlapping radius maps.
- QGIS: A free and open-source GIS software with a wide range of functionalities for spatial analysis.
3. How can I interpret the results of an overlapping radius map?
The interpretation of an overlapping radius map depends on the specific context and objectives. Key considerations include:
- Density of overlap: Areas with a high density of overlapping circles indicate high potential for interaction, competition, or collaboration.
- Area of overlap: The size and shape of the overlapping areas can provide insights into the nature and extent of influence.
- Spatial patterns: Visualizing the patterns of overlap can reveal trends and insights that might not be apparent from individual points.
Tips for Effective Overlapping Radius Map Creation
- Clearly define the purpose: Determine the specific objective of the map and select relevant data points and radii accordingly.
- Choose appropriate radius units: Select units (miles, kilometers, etc.) that align with the nature of the data and the scale of the analysis.
- Consider data accuracy: Ensure the accuracy and completeness of the data used to create the map.
- Experiment with different radii: Explore various radii to understand the impact of different influence levels.
- Use clear and concise labels: Label the points and circles with relevant information to enhance readability and understanding.
- Emphasize key areas: Highlight areas of high overlap or specific areas of interest using different colors, sizes, or patterns.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Spatial Understanding
Overlapping radius maps offer a powerful and versatile tool for visualizing and analyzing spatial relationships. By revealing the areas where multiple influences converge, they provide a richer understanding of proximity, competition, and collaboration within a geographic space. Their applications span diverse fields, empowering informed decision-making in areas ranging from urban planning and public health to retail and logistics. As spatial data becomes increasingly accessible, the use of overlapping radius maps is poised to grow, unlocking new insights and driving innovation across various domains.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Overlapping Radius Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
