Unveiling the Power of Radius-Based Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Radius-Based Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Radius-Based Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Radius-Based Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration

In the realm of spatial data visualization, maps with radius-based representations offer a powerful tool for understanding and communicating geographic information. These maps, often referred to as "circle maps" or "radius maps," utilize circles of varying sizes to depict quantitative data, providing an intuitive and visually engaging way to analyze spatial patterns and relationships. This article delves into the intricacies of radius-based maps, exploring their applications, benefits, and limitations, while highlighting their significance in various fields.
The Essence of Radius-Based Maps:
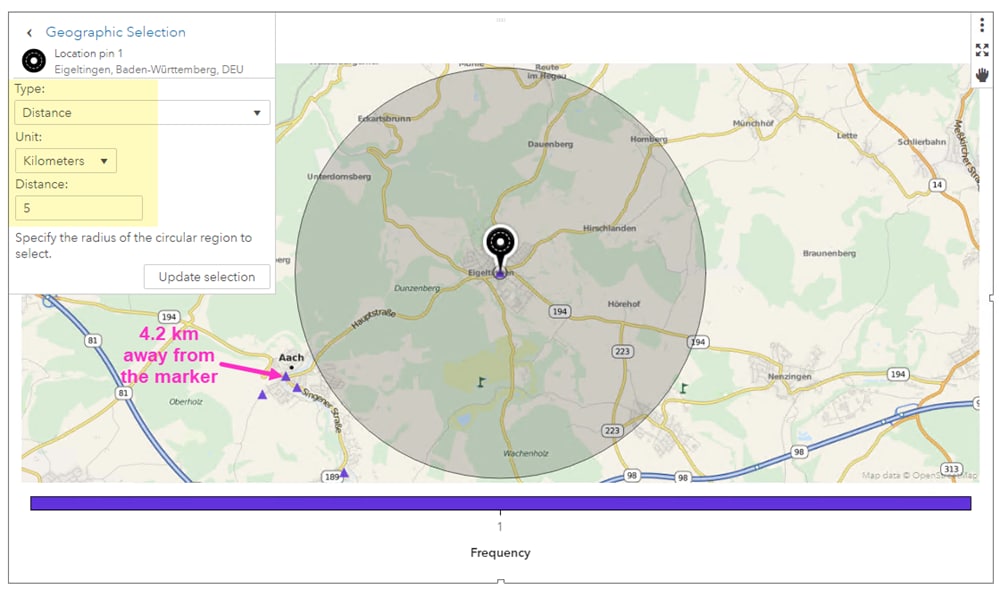
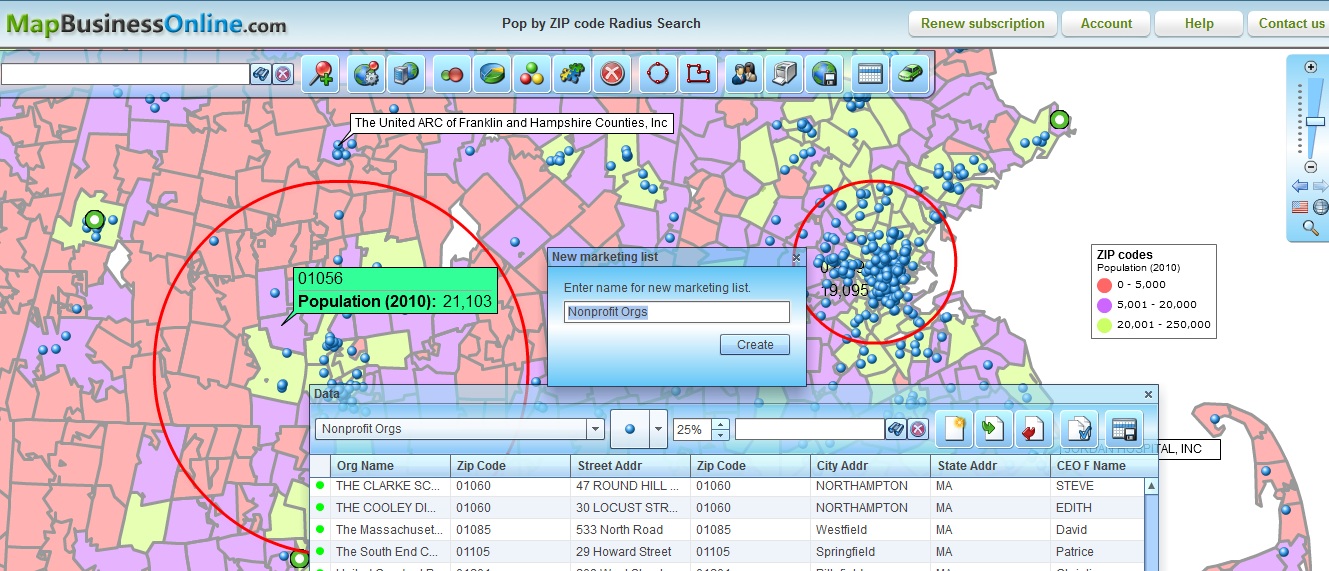
Radius-based maps employ circles to represent data points, with the size of each circle proportional to the value of the associated data. This simple yet effective technique allows for immediate visual interpretation of data distribution and magnitude. For instance, a map depicting population density could use larger circles to represent areas with higher population concentrations, while smaller circles would indicate areas with lower densities.
Applications Across Disciplines:
The versatility of radius-based maps extends across diverse disciplines, making them invaluable for:
- Urban Planning and Development: Visualizing population density, service coverage, and infrastructure distribution aids in urban planning, ensuring efficient resource allocation and promoting equitable development.
- Environmental Studies: Mapping pollution levels, wildlife distribution, and natural resource availability provides crucial insights into environmental conditions and informs conservation efforts.
- Epidemiology and Public Health: Identifying disease outbreaks, tracking the spread of infectious diseases, and visualizing healthcare access patterns are vital for public health initiatives.
- Business and Marketing: Analyzing customer demographics, market penetration, and competitor locations helps businesses make informed decisions regarding expansion, targeting, and resource allocation.
- Social Sciences and Research: Studying migration patterns, social inequalities, and cultural diffusion benefits from the ability of radius-based maps to visualize spatial relationships and trends.
Benefits of Radius-Based Maps:
The use of radius-based maps offers numerous advantages:
- Intuitive Visualization: The visual representation of data through circles is inherently intuitive, making it easy for viewers to grasp the spatial distribution and magnitude of data points.
- Effective Communication: Radius-based maps facilitate clear and concise communication of spatial information, enabling effective data dissemination to diverse audiences.
- Data Exploration and Discovery: By visualizing data in a spatial context, radius-based maps allow for the identification of patterns, trends, and outliers that might be missed in tabular data.
- Comparison and Contrast: Multiple datasets can be overlaid on a single map, enabling comparisons and contrasts between different data points and facilitating deeper analysis.
- Interactive Exploration: Radius-based maps can be integrated into interactive platforms, allowing users to zoom, pan, and filter data, enhancing user engagement and exploration.
Considerations and Limitations:
While radius-based maps offer significant advantages, certain limitations should be considered:
- Data Overlap: In areas with high data density, circles may overlap, obscuring data points and hindering accurate interpretation.
- Visual Distortion: The size of circles can create a visual bias, potentially exaggerating the importance of larger circles compared to smaller ones.
- Scale Sensitivity: The effectiveness of radius-based maps is dependent on the scale of the map and the density of data points.
- Data Accuracy and Reliability: The accuracy and reliability of the underlying data are crucial for the validity of any spatial representation, including radius-based maps.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What are the different types of radius-based maps?
- Proportional Symbol Maps: Use circles with sizes proportional to the data value.
- Graduated Symbol Maps: Utilize a range of circle sizes representing different data intervals.
- Dot Density Maps: Employ dots of uniform size, with the density of dots representing data values.
-
How can I create a radius-based map?
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software, such as ArcGIS, QGIS, and Google Earth Pro, provide tools for creating and manipulating radius-based maps.
-
What are the best practices for using radius-based maps?
- Choose an appropriate map projection and scale for the data being visualized.
- Select a color scheme that enhances visual clarity and avoids color blindness issues.
- Use a legend to clearly explain the relationship between circle size and data value.
- Include relevant context, such as boundaries, labels, and other relevant features.
-
What are the limitations of radius-based maps?
- As mentioned earlier, data overlap, visual distortion, scale sensitivity, and data accuracy are key limitations to consider.
Tips for Effective Use:
- Data Preparation: Ensure data is clean, accurate, and appropriately formatted for spatial analysis.
- Scale and Projection: Choose a map projection and scale that best suit the data and the intended audience.
- Color Selection: Use a color scheme that enhances visual clarity, avoids color blindness issues, and aligns with the data being visualized.
- Legend and Labels: Include a clear and concise legend explaining the relationship between circle size and data value.
- Contextual Information: Incorporate relevant contextual information, such as boundaries, labels, and other features, to enhance map readability and understanding.
- Interactive Elements: Consider incorporating interactive elements, such as zoom, pan, and filter options, to enhance user engagement and exploration.
Conclusion:
Radius-based maps provide a powerful and versatile tool for visualizing and communicating spatial data. Their ability to convey data distribution, magnitude, and relationships in an intuitive and visually engaging manner makes them invaluable across diverse disciplines. By understanding their strengths, limitations, and best practices, users can harness the power of radius-based maps to gain insights, facilitate informed decision-making, and effectively communicate spatial information. As technology continues to evolve, radius-based maps will undoubtedly play an increasingly important role in our understanding and interaction with the world around us.


![[Power Apps – Geospatial features] How to implement a radius-based location search ? - Power](https://www.powercommunity.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/radius-based-location-search-768x431.gif)
![[Power Apps – Geospatial features] How to implement a radius-based location search ? – XRM](https://meelamri.files.wordpress.com/2022/11/image-3.png)
![[Power Apps – Geospatial features] How to implement a radius-based location search ? – XRM](https://meelamri.files.wordpress.com/2022/11/image-2.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Radius-Based Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
