Unveiling the Power of Radius Overlay Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Radius Overlay Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Radius Overlay Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Radius Overlay Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
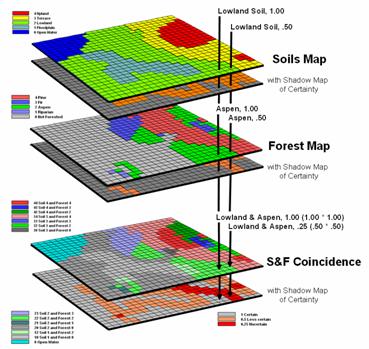
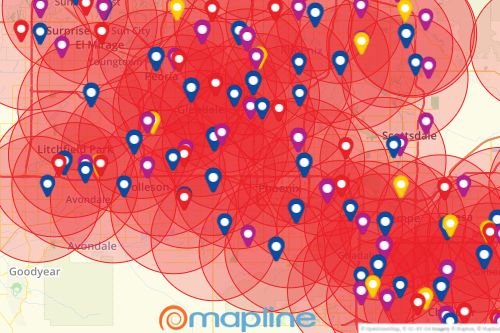
Radius overlay maps, also known as proximity maps or buffer maps, are powerful tools used to visualize and analyze spatial data by creating circular zones around specific locations. These maps offer a clear and intuitive representation of proximity, allowing users to understand and interpret spatial relationships within a given area.
The Fundamentals of Radius Overlay Maps:
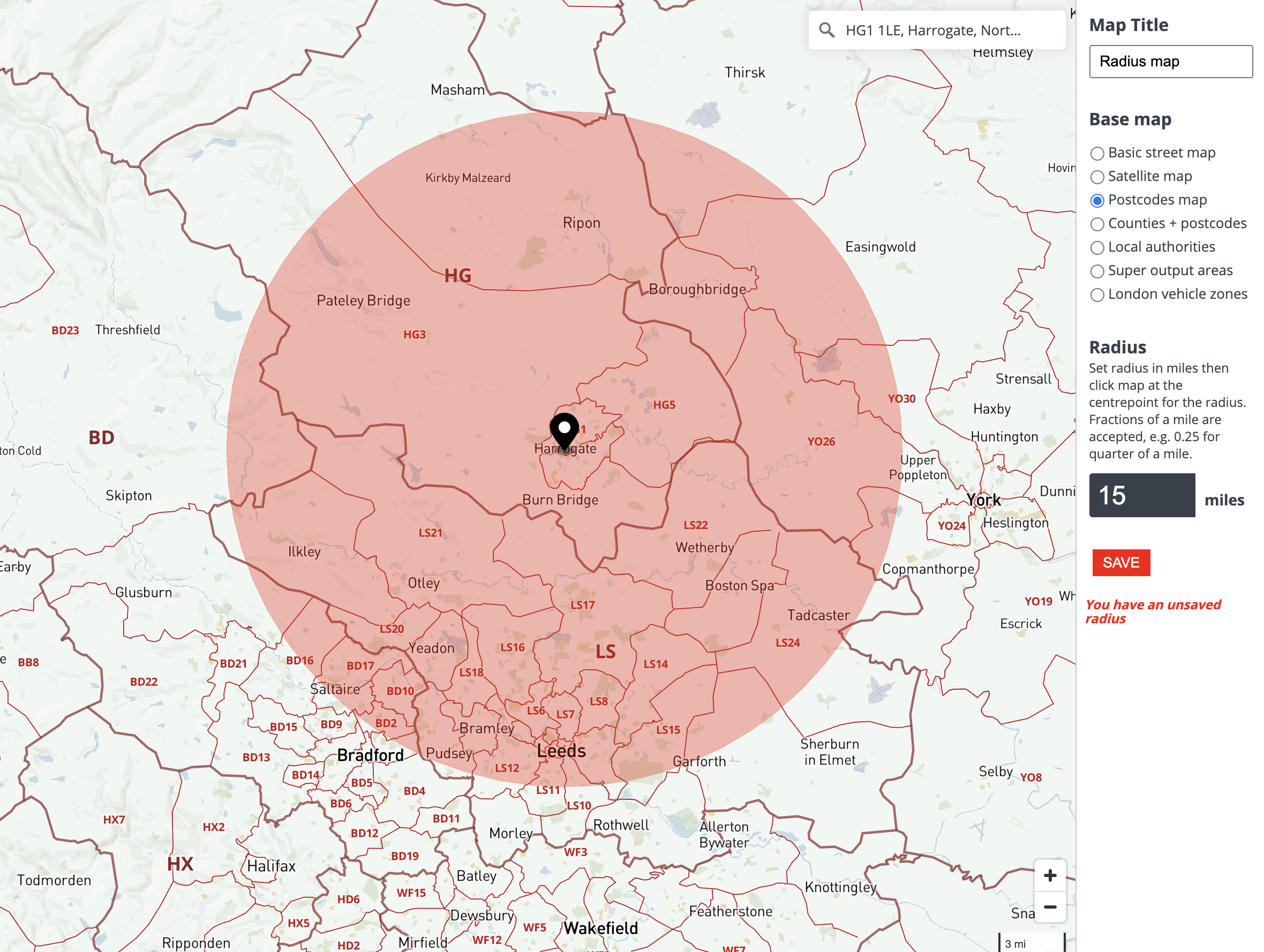
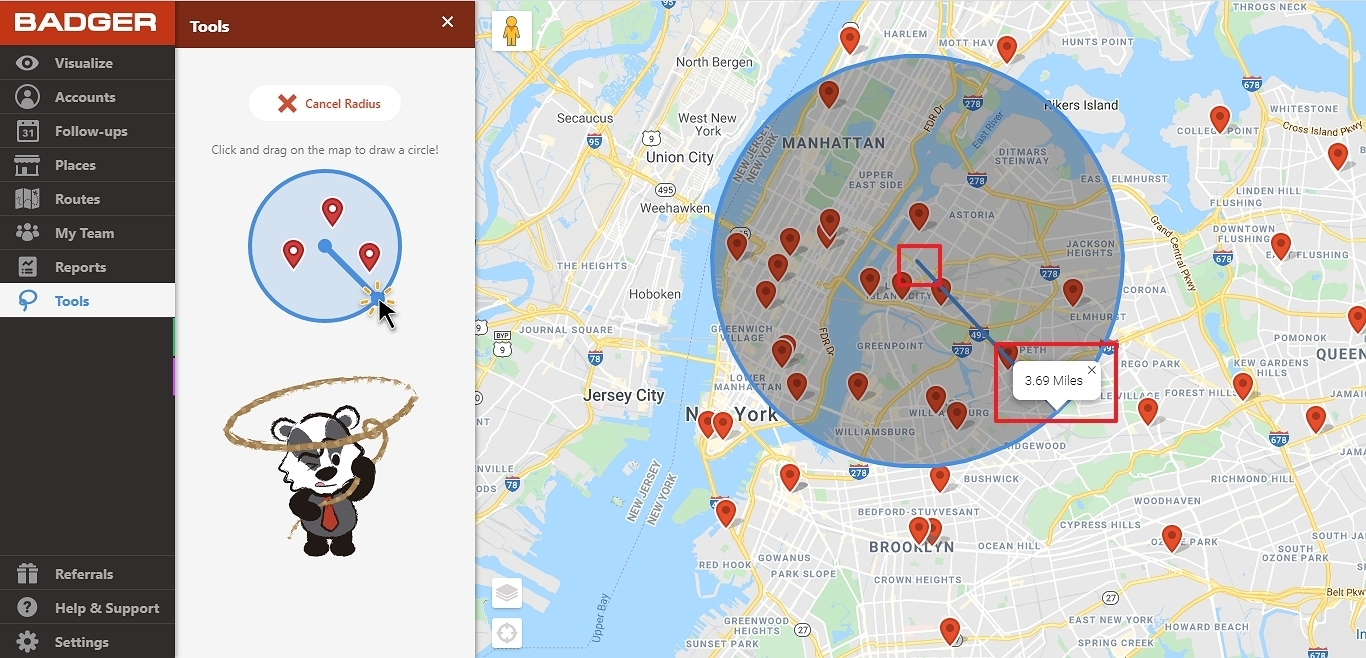
At their core, radius overlay maps function by overlaying circular zones, or buffers, onto a base map. These buffers represent a defined distance (radius) from a central point, such as a store, a school, or a healthcare facility. The size of the buffer can be adjusted based on the specific analysis being conducted. For example, a buffer of 5 miles around a school could be used to visualize the area served by that school, while a buffer of 100 meters around a retail store could illustrate its immediate customer catchment area.
Applications of Radius Overlay Maps:
The versatility of radius overlay maps makes them valuable across various industries and fields, including:
-
Business and Marketing:
- Market Analysis: Identifying potential customer bases by visualizing the proximity of residential areas, businesses, or demographic groups to a particular location.
- Site Selection: Evaluating the suitability of potential locations for new stores, restaurants, or other businesses based on factors like proximity to competitors, customers, or transportation hubs.
- Targeted Marketing Campaigns: Developing geographically targeted marketing campaigns by identifying areas within a specific radius of a business or event.
-
Urban Planning and Development:
- Accessibility Analysis: Assessing the accessibility of public services, such as schools, hospitals, and transportation infrastructure, to different areas within a city.
- Neighborhood Planning: Understanding the spatial relationships between residential areas, commercial zones, and public amenities to inform development plans.
- Disaster Response: Identifying areas at risk from natural disasters based on their proximity to critical infrastructure or vulnerable populations.
-
Environmental Management:
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Visualizing the potential impact of development projects on surrounding ecosystems by overlaying buffers around sensitive areas.
- Wildlife Conservation: Understanding the spatial distribution of wildlife populations and identifying areas that require protection.
- Pollution Monitoring: Mapping the spread of pollution from industrial sources or other point sources.
-
Public Health and Healthcare:
- Disease Surveillance: Identifying areas with high concentrations of disease cases and potential hotspots for disease outbreaks.
- Healthcare Access: Assessing the accessibility of healthcare services to different populations based on their proximity to hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare facilities.
- Emergency Response: Optimizing the deployment of emergency services by identifying the areas within a specific radius of an incident.
-
Law Enforcement and Security:
- Crime Mapping: Identifying areas with high crime rates and potential hotspots for criminal activity.
- Security Planning: Evaluating the effectiveness of security measures by visualizing the areas within a specific radius of protected assets.
- Search and Rescue Operations: Optimizing search patterns by identifying areas within a specific radius of a missing person or object.
Benefits of Using Radius Overlay Maps:
- Enhanced Spatial Understanding: Radius overlay maps provide a clear and intuitive way to visualize spatial relationships, enabling users to quickly grasp the proximity of different locations and features.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: By overlaying buffers on spatial data, users can gain valuable insights into the relationships between different locations and make informed decisions based on proximity and distance.
- Improved Communication and Collaboration: Radius overlay maps offer a common language for communicating spatial information, facilitating collaboration among different stakeholders.
- Efficient Analysis and Visualization: These maps streamline the process of analyzing spatial data and provide a visual representation of complex relationships, making it easier to identify patterns and trends.
Key Features of Radius Overlay Maps:
- Customizable Buffer Size: The radius of the buffer can be adjusted to represent different distances, allowing users to analyze spatial relationships at varying scales.
- Multiple Buffer Layers: Multiple buffers can be overlaid on the same map to represent different locations or distances, enabling the analysis of complex spatial relationships.
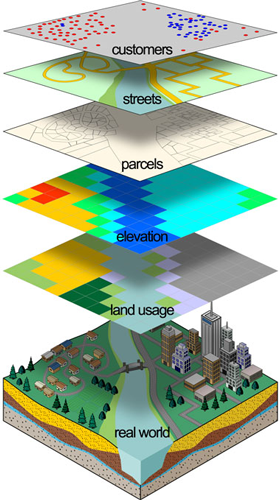
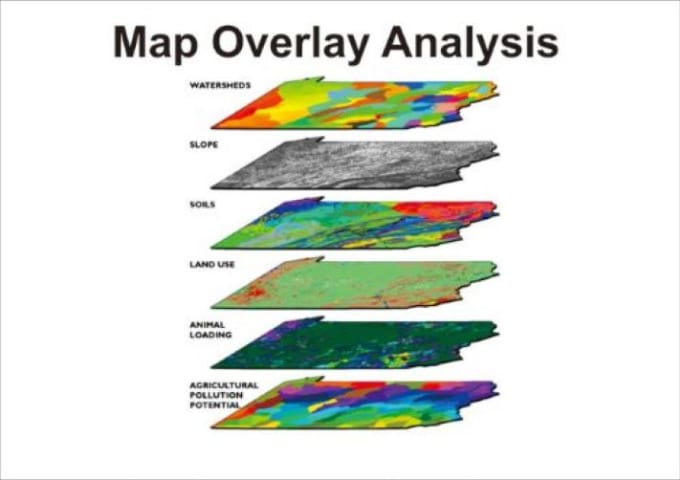
- Data Integration: Radius overlay maps can be integrated with other spatial data layers, such as population density, demographics, or environmental conditions, to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the area being analyzed.
- Interactive Visualization: Many mapping software programs allow users to interact with radius overlay maps, enabling them to zoom in, pan, and explore the data in detail.
FAQs about Radius Overlay Maps:
Q: What are the different types of radius overlay maps?
A: Radius overlay maps can be categorized based on their application and purpose. Common types include:
- Proximity maps: These maps highlight the proximity of points of interest to a specific location.
- Buffer maps: These maps create circular zones around specific locations, representing a defined distance.
- Drive time maps: These maps visualize the areas reachable within a specific drive time from a starting point.
- Service area maps: These maps illustrate the service area of a business or organization, highlighting the areas within a specific radius of its facilities.
Q: What software can be used to create radius overlay maps?
A: A wide range of software programs can be used to create radius overlay maps, including:
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software like ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo are powerful tools for creating and analyzing radius overlay maps.
- Mapping Platforms: Online mapping platforms like Google Maps, Mapbox, and Leaflet allow users to create simple radius overlay maps.
- Spreadsheet Software: Spreadsheets like Microsoft Excel can be used to create basic radius overlay maps using formulas and functions.
Q: What are some best practices for creating radius overlay maps?
A: Creating effective radius overlay maps requires careful consideration of the following:
- Define the purpose of the map: Clearly define the objective of the map and the specific information it aims to convey.
- Choose the appropriate map projection: Select a map projection that minimizes distortion and accurately represents the area of interest.
- Select the correct buffer size: Choose a buffer size that is relevant to the analysis being conducted and the scale of the map.
- Use clear and concise labels: Ensure that all labels and symbols are legible and easily understood.
- Consider the target audience: Design the map to be accessible and informative for the intended audience.
Tips for Using Radius Overlay Maps Effectively:
- Start with a clear objective: Define the specific question you are trying to answer with the map.
- Choose the appropriate data: Select data layers that are relevant to your analysis and the scale of the map.
- Experiment with different buffer sizes: Try different buffer sizes to see how they affect the results.
- Use color and symbology effectively: Use color and symbology to highlight key features and patterns.
- Provide context and interpretation: Include a legend, a scale bar, and a brief explanation of the map’s purpose and findings.
Conclusion:
Radius overlay maps are valuable tools for visualizing and analyzing spatial data, offering a clear and intuitive representation of proximity and distance. By understanding the fundamentals of these maps and their various applications, users can leverage their power to gain valuable insights, make informed decisions, and communicate spatial information effectively. As spatial data continues to grow in volume and complexity, radius overlay maps will remain an essential tool for navigating and interpreting the world around us.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Radius Overlay Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
