Unveiling the Power of Scale: Understanding the Crucial Role of Map Scale in Spatial Representation
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Scale: Understanding the Crucial Role of Map Scale in Spatial Representation
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Scale: Understanding the Crucial Role of Map Scale in Spatial Representation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Scale: Understanding the Crucial Role of Map Scale in Spatial Representation
Maps, as visual representations of the Earth’s surface, are indispensable tools in a myriad of fields, from navigation and exploration to urban planning and environmental analysis. However, their effectiveness hinges on a fundamental concept: scale. Map scale, a crucial element in cartography, establishes the relationship between distances on a map and their corresponding distances on the real world. It acts as a bridge, enabling us to comprehend the vastness of our planet and its intricacies within a manageable format.
Defining the Essence of Map Scale:
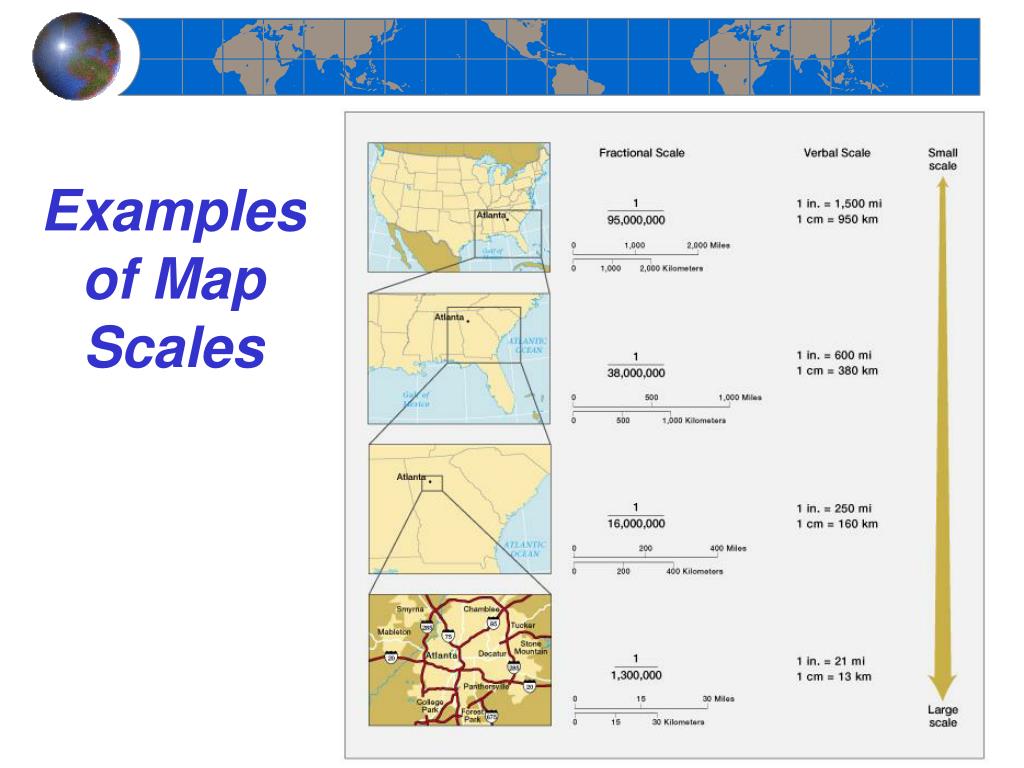
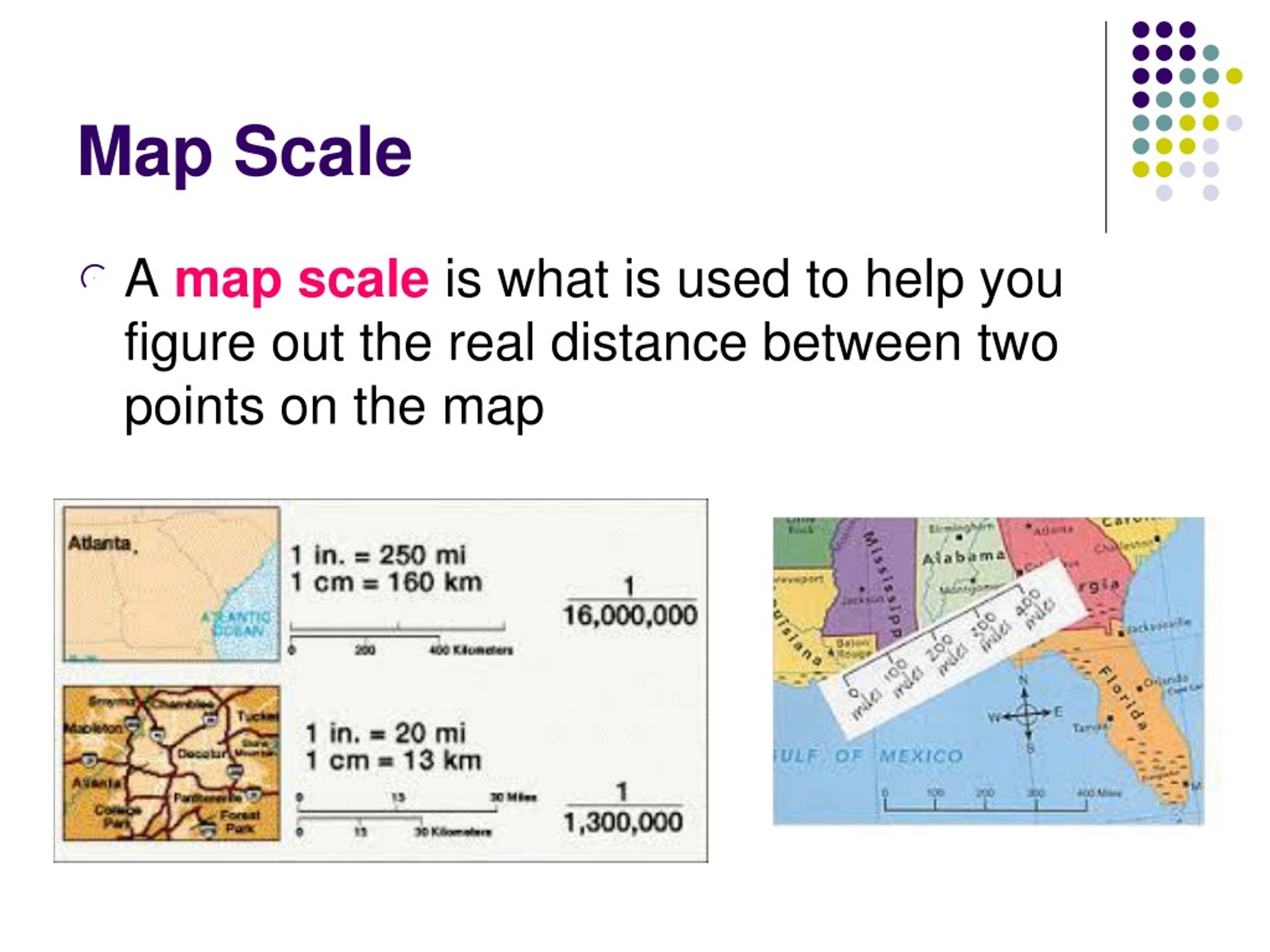
Map scale, essentially a ratio, quantifies the reduction of the real world on a map. It signifies the extent to which distances on a map are shrunk compared to their actual counterparts. This ratio can be expressed in three primary ways:
- Verbal Scale: This method presents the scale as a simple statement, often in the form of "1 inch equals 1 mile" or "1 centimeter equals 10 kilometers." This straightforward representation provides a clear understanding of the relationship between map units and real-world units.
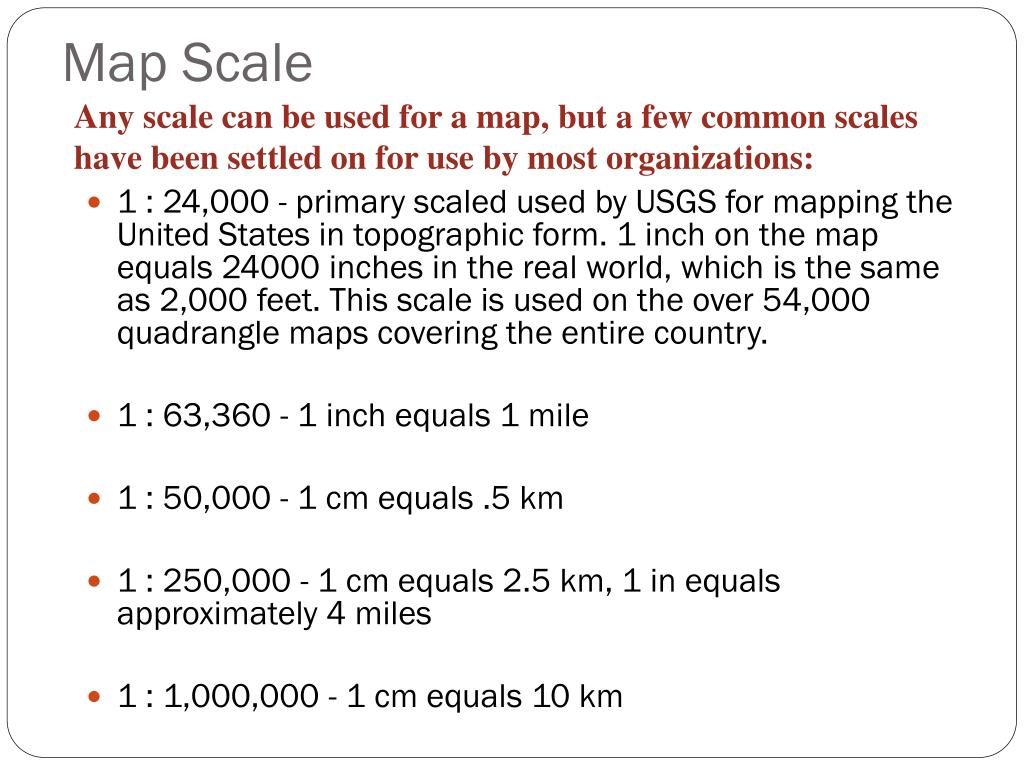
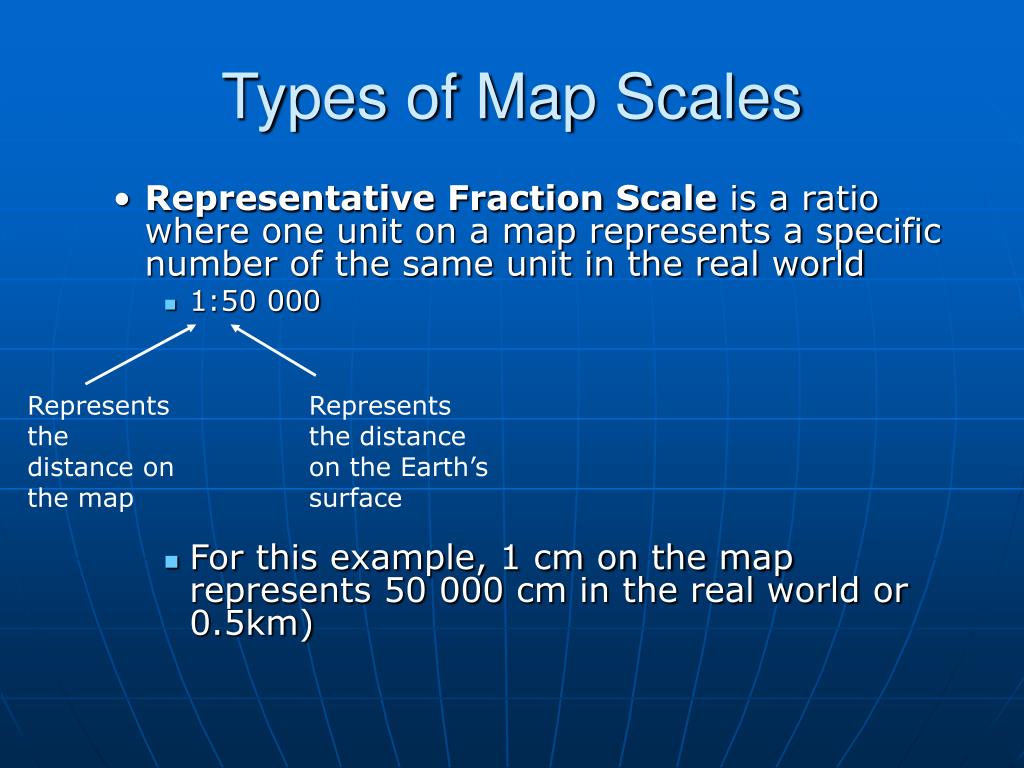
- Representative Fraction (RF): This method expresses the scale as a fraction, such as 1:100,000. The numerator represents one unit on the map, while the denominator represents the equivalent number of units in reality. This format allows for precise calculations and comparisons between different scales.
- Graphic Scale: This method utilizes a visual bar, divided into segments representing specific distances on the map. Each segment corresponds to a specific distance on the ground, allowing for quick and intuitive estimation of distances without complex calculations.
Understanding the Implications of Scale:
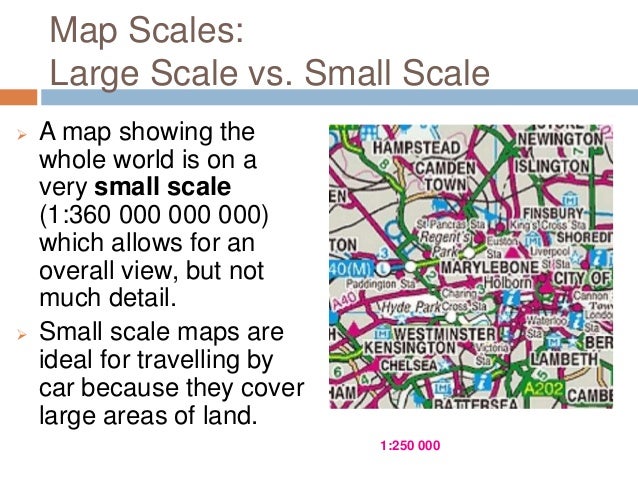
The choice of map scale significantly influences the level of detail and the area that can be represented. A large-scale map, with a smaller ratio (e.g., 1:10,000), depicts a smaller area but with greater detail, suitable for local planning or navigation within a specific region. Conversely, a small-scale map, with a larger ratio (e.g., 1:10,000,000), covers a vast area but sacrifices detail, suitable for depicting global patterns or long-distance travel.
Benefits of Understanding Map Scale:
- Accurate Measurement: Map scale enables accurate measurement of distances, areas, and other spatial attributes on a map. By knowing the scale, one can directly translate map measurements to real-world distances.
- Effective Spatial Analysis: Understanding map scale facilitates spatial analysis, allowing for comparisons between different areas, identification of spatial patterns, and assessment of the relative size and importance of various features.
- Informed Decision-Making: Map scale plays a crucial role in informed decision-making, particularly in fields like urban planning, environmental management, and resource allocation. By understanding the scale of a map, stakeholders can assess the feasibility and impact of proposed projects or policies.
- Enhanced Communication: Map scale serves as a common language, facilitating communication and understanding across disciplines. By standardizing the representation of spatial information, it ensures consistent interpretation and avoids ambiguity.
Navigating the Complexity of Map Scale:
While map scale is a fundamental concept, its practical application can be nuanced. Factors such as map projection, distortion, and the intended purpose of the map can influence the selection and interpretation of scale.
Map Projection and Distortion:
The Earth, being a sphere, cannot be perfectly represented on a flat map without some degree of distortion. Map projections, mathematical formulas used to transform the Earth’s curved surface onto a plane, introduce varying levels of distortion depending on the chosen projection. These distortions can affect distances, areas, shapes, and directions on the map, necessitating careful consideration of the chosen projection and its inherent limitations.
Scale Variation and Map Accuracy:
Maps are often created at a specific scale, but due to the inherent limitations of cartographic representation, scale can vary across the map. This variation, known as scale distortion, arises from the inherent challenges of representing a curved surface on a flat plane. Understanding scale variation is crucial for accurate measurements and interpretations, particularly in maps with large areas or significant geographical features.
The Importance of Scale in Different Applications:
- Navigation: For navigation, large-scale maps are essential, providing detailed information about roads, landmarks, and other features relevant to local travel.
- Urban Planning: Urban planners rely on maps of various scales to assess land use, infrastructure, and population density, facilitating informed decision-making for urban development.
- Environmental Management: Environmental studies often utilize maps to analyze ecological patterns, assess environmental hazards, and plan conservation efforts. The choice of scale depends on the specific environmental issue being investigated.
- Resource Allocation: Resource management, such as water allocation or mineral extraction, requires accurate spatial data and maps at appropriate scales to ensure efficient and sustainable utilization.
FAQs on Map Scale:
1. What is the difference between large-scale and small-scale maps?
Large-scale maps represent a smaller area with greater detail, while small-scale maps cover a wider area with less detail.
2. How can I determine the scale of a map?
The scale of a map can be identified by looking for a verbal scale statement, a representative fraction, or a graphic scale bar.
3. Why is scale important in map interpretation?
Scale enables accurate measurement, spatial analysis, informed decision-making, and effective communication of spatial information.
4. How can I use scale to calculate distances on a map?
By knowing the scale, you can directly convert distances measured on the map to real-world distances using the appropriate units of measurement.
5. What are some common examples of map scales?
Common examples include 1:10,000 (large scale), 1:100,000 (medium scale), and 1:1,000,000 (small scale).
Tips for Understanding and Using Map Scale:
- Pay attention to the scale: Always carefully check the scale of a map before using it to ensure it is appropriate for your needs.
- Use a ruler: A ruler can be used to measure distances on a map and convert them to real-world distances using the map scale.
- Consider the purpose of the map: The intended purpose of the map should guide the selection of an appropriate scale.
- Be aware of distortion: Understand the limitations of map projections and the potential for scale distortion, especially in maps covering large areas.
- Consult multiple maps: When working with complex spatial data, it is often helpful to consult maps at different scales to obtain a comprehensive understanding of the area.
Conclusion:
Map scale is a fundamental concept in cartography, acting as the cornerstone for understanding and interpreting spatial information. By comprehending the relationship between map distances and real-world distances, we unlock the power of maps to analyze patterns, make informed decisions, and navigate the complexities of our world. From navigating city streets to planning global conservation efforts, map scale plays a vital role in our understanding and interaction with the spatial dimensions of our planet.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Scale: Understanding the Crucial Role of Map Scale in Spatial Representation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
