Unveiling the Power of Visual Representation: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Scales
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Visual Representation: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Scales
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Visual Representation: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Scales. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Visual Representation: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Scales

Heat maps, with their vibrant color gradients, have become ubiquitous in various fields, offering a powerful tool for visualizing data and conveying complex information with ease. At the heart of this visual language lies the heat map scale, a crucial element that dictates the interpretation and understanding of the data presented.
This guide delves into the intricacies of heat map scales, exploring their fundamental principles, diverse applications, and the critical role they play in data visualization.
Defining the Heat Map Scale: The Key to Interpretation
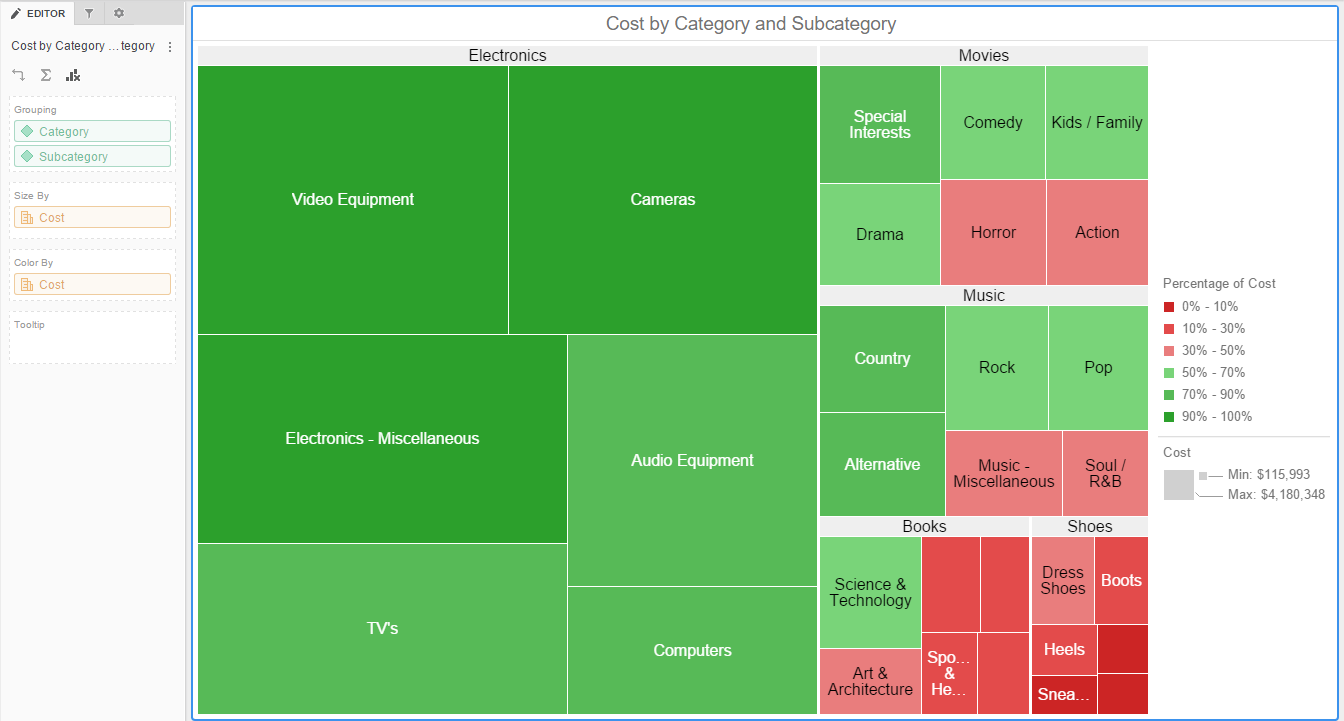
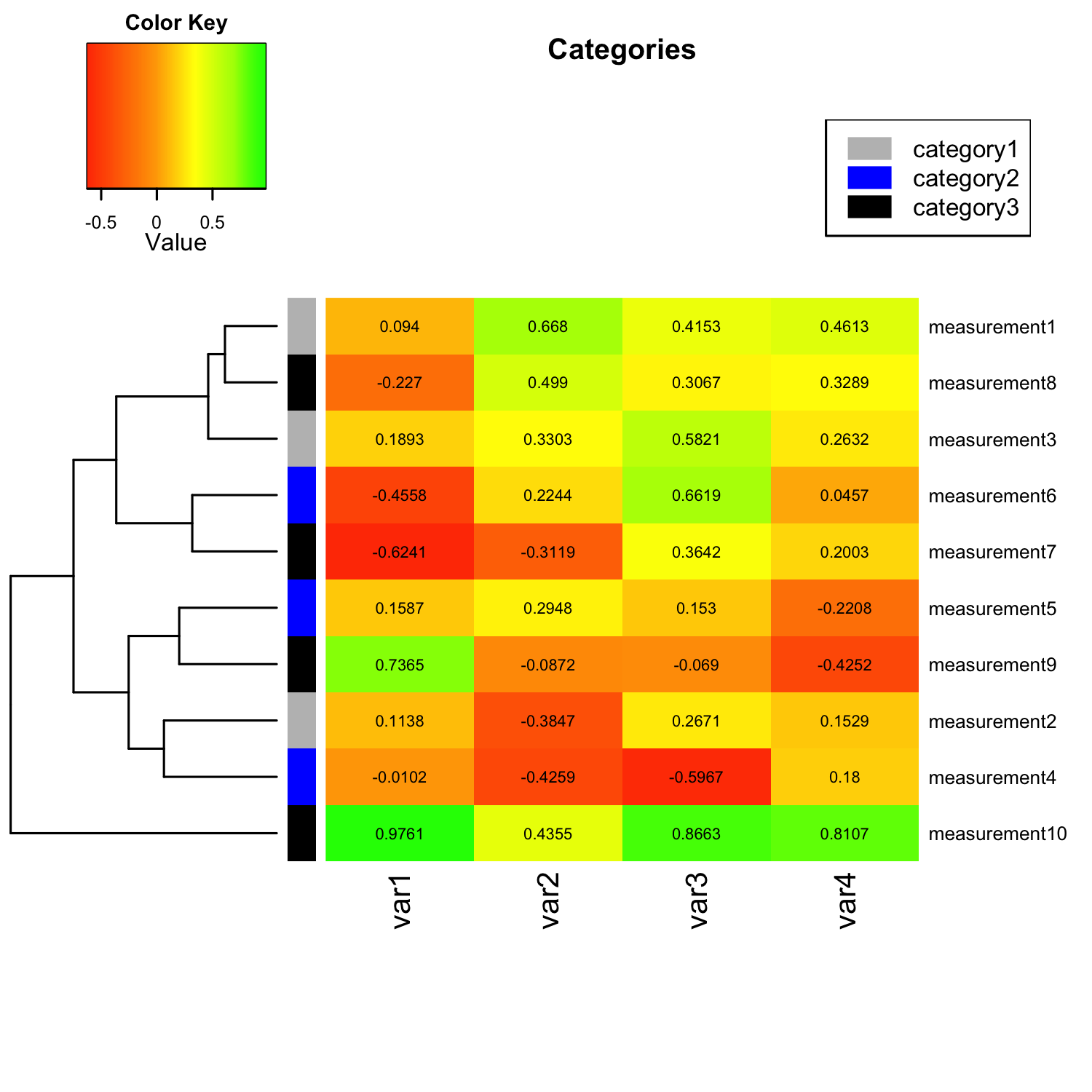
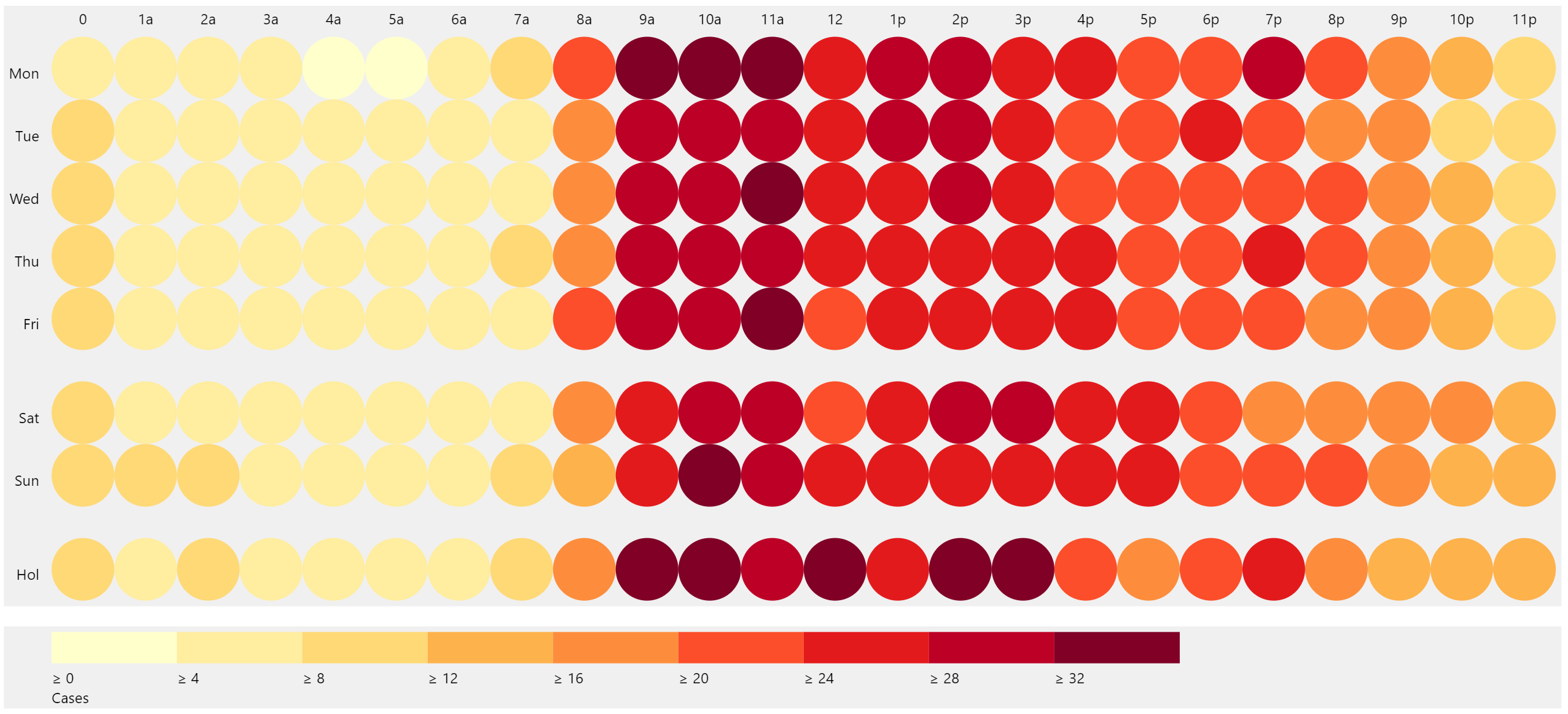
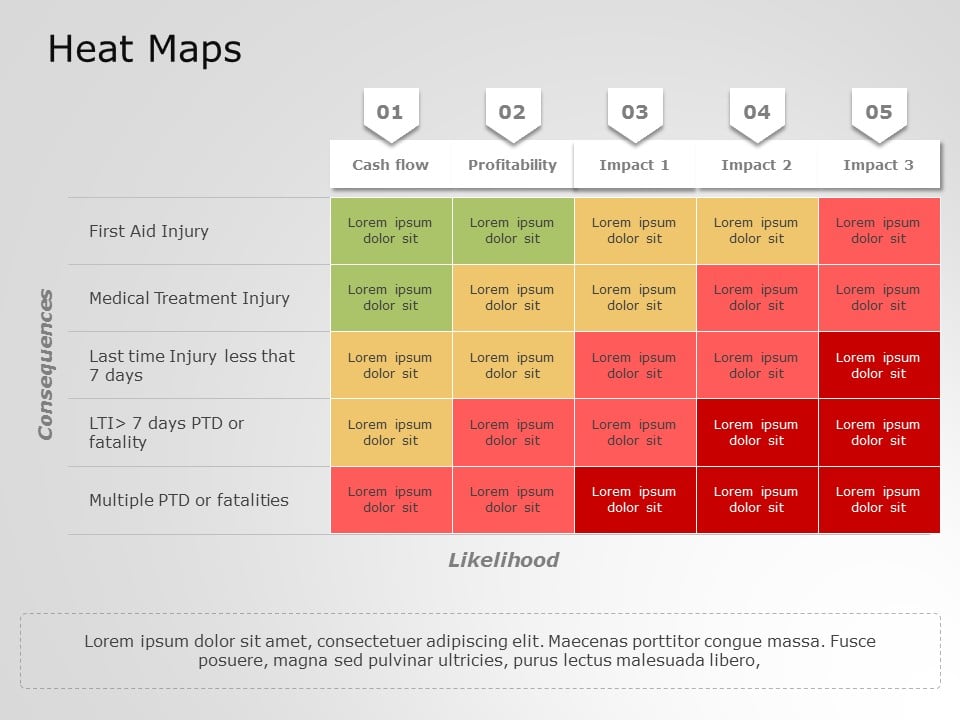
A heat map scale, also known as a color scale or legend, is a visual representation that translates numerical data into a spectrum of colors. Each color on the scale corresponds to a specific range of values, allowing viewers to quickly grasp the distribution and magnitude of data points within a visual representation.
Imagine a heat map depicting website traffic. A red color might represent high traffic, while blue indicates low traffic. The heat map scale would then display the corresponding traffic values for each color, enabling viewers to understand the specific traffic levels associated with different areas on the website.
The Importance of Choosing the Right Scale
The selection of an appropriate heat map scale is paramount to ensuring accurate and effective data interpretation. A poorly chosen scale can lead to misleading conclusions and hinder the effectiveness of the visualization. Here are key factors to consider:
- Data Range: The scale should encompass the full range of data values, ensuring that all data points are represented accurately.
- Data Distribution: The scale should reflect the distribution of data values, avoiding skewed representations.
- Color Palette: The choice of colors should be visually appealing and provide clear contrast between different data ranges. Consider using colorblind-friendly palettes for accessibility.
- Clarity and Simplicity: The scale should be clear and easy to understand, avoiding unnecessary complexity.
Types of Heat Map Scales
Heat map scales come in various forms, each offering distinct advantages and limitations:
- Linear Scales: These scales represent data values proportionally, with a continuous gradient from the lowest to the highest value. They are commonly used for data with a linear distribution.
- Logarithmic Scales: These scales represent data values on a logarithmic scale, compressing large values and emphasizing smaller differences. They are suitable for data with a wide range of values.
- Diverging Scales: These scales represent data values around a central point, with contrasting colors representing deviations from the midpoint. They are useful for highlighting deviations or anomalies in data.
- Sequential Scales: These scales use a single color gradient to represent data values, with darker shades indicating higher values. They are effective for visualizing trends or patterns in data.
Applications of Heat Map Scales: Across Diverse Fields
Heat map scales have found widespread applications in diverse fields, revolutionizing data visualization and analysis:
- Business Analytics: Identifying customer segments, understanding website traffic patterns, and optimizing marketing campaigns.
- Finance: Analyzing market trends, identifying investment opportunities, and assessing risk.
- Healthcare: Diagnosing diseases, monitoring patient health, and optimizing treatment plans.
- Environmental Science: Monitoring pollution levels, predicting natural disasters, and understanding climate change.
- Social Sciences: Analyzing demographic trends, mapping social networks, and understanding social phenomena.
FAQs: Demystifying the Heat Map Scale
Q: What are the benefits of using a heat map scale?
A: Heat map scales offer several benefits, including:
- Enhanced Visual Clarity: They present complex data in a visually appealing and easily understandable format.
- Improved Data Interpretation: They facilitate quick and accurate interpretation of data trends and patterns.
- Effective Communication: They enable effective communication of data insights to diverse audiences.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: They provide valuable insights that support informed decision-making.
Q: How can I choose the right heat map scale for my data?
A: Consider the following factors when choosing a heat map scale:
- Data type: The nature of your data (linear, logarithmic, etc.) will dictate the appropriate scale.
- Data range: The scale should encompass the full range of values.
- Data distribution: The scale should reflect the distribution of values.
- Visual clarity: Choose colors and a scale that provide clear contrast and readability.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when using heat map scales?
A: Avoid the following pitfalls:
- Using too many colors: This can overwhelm viewers and hinder comprehension.
- Choosing inappropriate color palettes: Ensure the palette is visually appealing and provides clear contrast.
- Ignoring data distribution: The scale should accurately reflect the distribution of values.
- Over-interpreting data: Avoid drawing conclusions based solely on the visual representation; always consider the underlying data.
Tips for Creating Effective Heat Map Scales
- Keep it simple: Avoid overcomplicating the scale with unnecessary details.
- Use clear labels: Label the scale clearly and concisely.
- Consider accessibility: Use colorblind-friendly palettes and ensure sufficient contrast.
- Test the scale: Test the scale with different audiences to ensure it is easily understood.
Conclusion: The Power of Visual Insights
Heat map scales are essential components of data visualization, enabling the effective communication and interpretation of complex information. By understanding the principles and applications of heat map scales, individuals can leverage their power to gain valuable insights, make informed decisions, and communicate data effectively. As data visualization continues to evolve, heat map scales will undoubtedly play a vital role in shaping the future of data analysis and communication.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Visual Representation: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Scales. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
