Unveiling the Secrets of Map Scale: A Comprehensive Guide to Calculating Area on Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of Map Scale: A Comprehensive Guide to Calculating Area on Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of Map Scale: A Comprehensive Guide to Calculating Area on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of Map Scale: A Comprehensive Guide to Calculating Area on Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Secrets of Map Scale: A Comprehensive Guide to Calculating Area on Maps
- 3.1 Understanding the Foundation: Map Scale and Its Significance
- 3.2 Decoding the Area Formula: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.3 Beyond the Basics: Addressing Common Challenges
- 3.4 Applications: Where Map Scale Area Formula Shines
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Area Calculation
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Understanding the World
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Secrets of Map Scale: A Comprehensive Guide to Calculating Area on Maps
Maps, those ubiquitous representations of the world, serve as powerful tools for navigation, planning, and understanding our surroundings. They condense vast landscapes into manageable formats, allowing us to visualize distances, explore unfamiliar territories, and even analyze spatial relationships. However, the accuracy of these representations hinges on a crucial concept: map scale.
Map scale defines the relationship between distances on a map and their corresponding distances on the ground. It essentially provides a conversion factor, enabling us to translate measurements from the map to the real world. This is where the area formula comes into play, offering a precise method to calculate the actual area of features depicted on a map.
Understanding the Foundation: Map Scale and Its Significance
Map scales are expressed in various ways, each conveying the same fundamental relationship:
- Verbal Scale: A simple statement like "1 inch equals 1 mile" or "1 centimeter equals 10 kilometers."
- Representative Fraction (RF): A ratio expressing the map distance as a fraction of the ground distance, such as 1:100,000 or 1:25,000. This means one unit on the map represents 100,000 or 25,000 units on the ground, respectively.
- Graphic Scale: A visual representation of the scale, typically a bar with marked distances corresponding to actual ground distances.
The choice of scale depends on the purpose of the map. Large-scale maps, with smaller RF values, provide detailed representations of smaller areas, ideal for urban planning or engineering projects. Conversely, small-scale maps, with larger RF values, encompass wider areas, suitable for regional or global analysis.
Decoding the Area Formula: A Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating the area of a feature on a map involves a simple yet powerful formula:
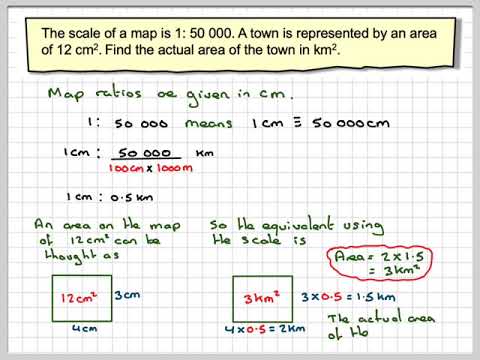
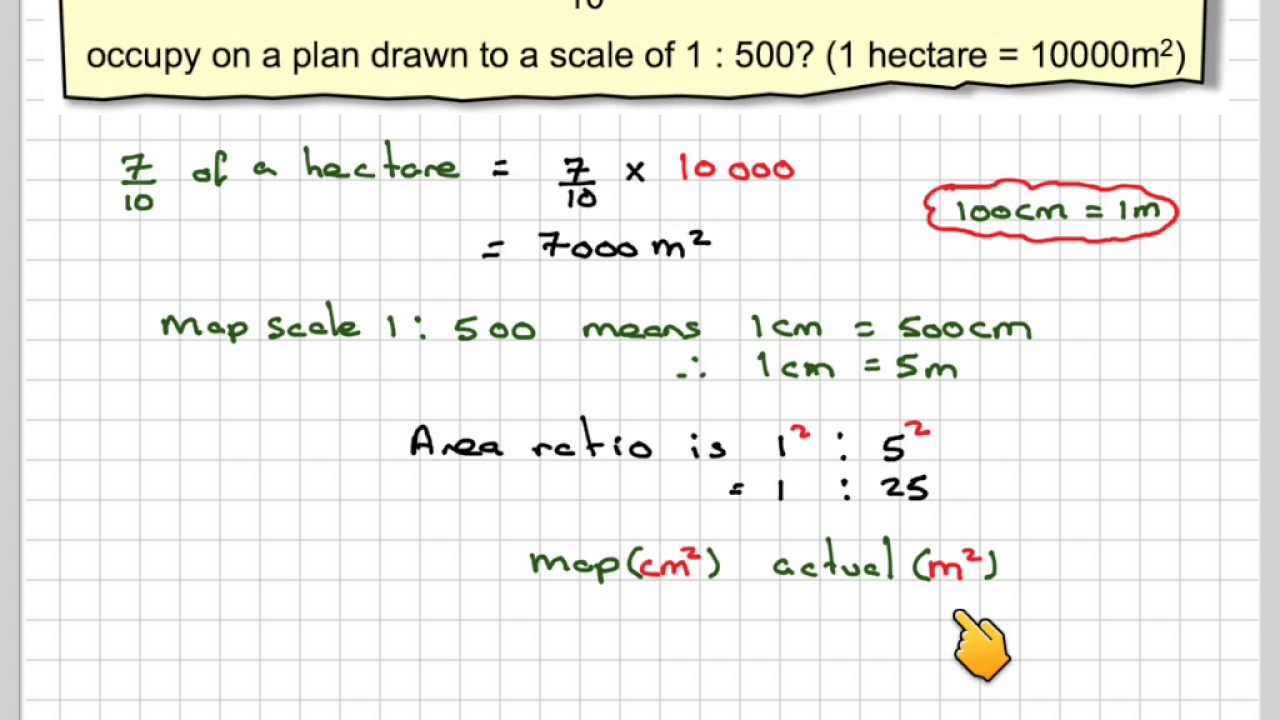
Area on Map (in square units) x (Scale Factor)² = Actual Area (in square units)
The "Scale Factor" is the denominator of the representative fraction (RF). For example, if the RF is 1:100,000, the Scale Factor is 100,000.
Let’s illustrate this with an example:
Imagine a rectangular park on a map with dimensions of 5 cm by 3 cm, and the map scale is 1:25,000.
- Calculate the area on the map: 5 cm x 3 cm = 15 square cm.
- Determine the Scale Factor: The RF is 1:25,000, so the Scale Factor is 25,000.
- Apply the formula: 15 square cm x (25,000)² = 9,375,000,000 square cm.
- Convert to more practical units: 9,375,000,000 square cm = 937,500 square meters.
Therefore, the actual area of the park is 937,500 square meters.
Beyond the Basics: Addressing Common Challenges
While the formula itself is straightforward, calculating areas on maps can present various challenges:
- Irregular Shapes: Many real-world features have irregular shapes, making direct measurement difficult. In such cases, divide the shape into smaller, regular shapes (rectangles, triangles) and calculate the area of each. Summing these individual areas gives the total area of the irregular feature.
- Curved Boundaries: Features with curved boundaries require approximation techniques. One common method is to divide the curved boundary into smaller straight segments, creating a series of trapezoids. The sum of the areas of these trapezoids approximates the area of the curved feature.
- Scale Variation: Some maps, particularly older ones, might have varying scales across different sections. In such situations, it’s crucial to identify the relevant scale for each section and apply the formula accordingly.
Applications: Where Map Scale Area Formula Shines
The ability to calculate areas from maps holds immense practical value across various disciplines:
- Land Management: Determining land sizes for property transactions, urban planning, and resource management.
- Environmental Science: Assessing forest cover, estimating wildlife populations, and analyzing land use patterns.
- Geography and Cartography: Mapping and analyzing spatial data, understanding population density, and studying geographical phenomena.
- Disaster Management: Evaluating disaster impact zones, planning evacuation routes, and assessing infrastructure damage.
- Military Operations: Determining target areas, planning troop movements, and analyzing terrain features.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What happens if the map scale is not provided?
Without a known map scale, calculating the actual area is impossible. You need the scale to convert the map measurements to real-world dimensions.
2. Can I use different units for map measurements and actual area?
Yes, but ensure consistency in unit conversions. If map measurements are in centimeters and you want the actual area in square meters, convert the map measurements to meters before applying the formula.
3. How accurate are area calculations based on map scale?
The accuracy of area calculations depends on the map scale and the complexity of the feature. Larger scales generally offer greater accuracy, while irregular shapes and curved boundaries introduce potential for error.
4. Are there any online tools for calculating area from maps?
Yes, several online tools and software applications can assist in calculating areas from maps. These tools often provide options for different map scales, units, and shape types.
Tips for Effective Area Calculation
- Choose the appropriate map scale: Select a map with a scale suitable for the desired level of detail and accuracy.
- Use precise measurements: Employ accurate measuring tools like rulers or calipers to minimize measurement errors.
- Consider map projections: Different map projections can distort areas, particularly at larger scales. If necessary, consult resources on map projections to adjust area calculations.
- Employ technology: Explore online tools and software applications to simplify and enhance area calculations.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Understanding the World
The map scale area formula serves as a fundamental tool for interpreting and analyzing information presented on maps. It empowers us to translate the two-dimensional representations into meaningful real-world measurements, providing valuable insights for various applications. By understanding the formula, its limitations, and its applications, we can unlock the full potential of maps as powerful tools for understanding our world.

![Map Scales [ Area ] – GeoGebra](https://www.geogebra.org/resource/PwbGM5yT/ijVIMbBQClZkw4Yi/material-PwbGM5yT.png)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of Map Scale: A Comprehensive Guide to Calculating Area on Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
