Unveiling the World Within 70 Miles: A Comprehensive Guide to Radius Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the World Within 70 Miles: A Comprehensive Guide to Radius Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World Within 70 Miles: A Comprehensive Guide to Radius Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the World Within 70 Miles: A Comprehensive Guide to Radius Maps
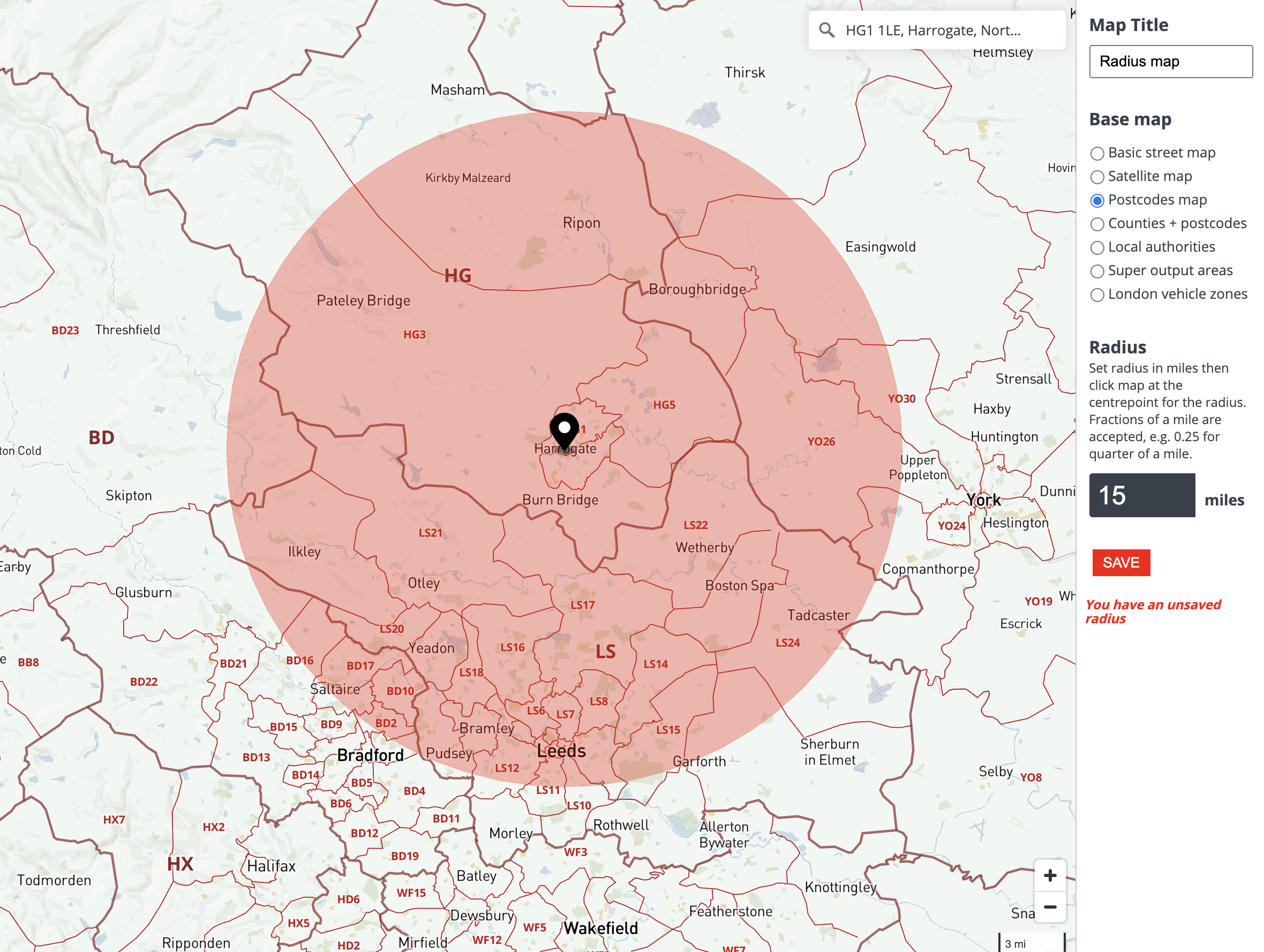
The concept of a radius map, specifically a 70-mile radius map, might seem simple at first glance. It is, after all, a visual representation of a circular area encompassing everything within a 70-mile distance from a central point. However, this seemingly straightforward tool holds immense potential for various applications, offering valuable insights and facilitating informed decision-making in diverse fields.
This article delves into the intricacies of 70-mile radius maps, exploring their construction, uses, and significance. We will examine the underlying principles, delve into specific applications, and discuss the benefits and challenges associated with this powerful visualization tool.
Understanding the Basics
At its core, a 70-mile radius map is a cartographic representation of a circular area with a 70-mile radius. The central point of this circle, often referred to as the origin, serves as the reference point from which the distance is measured. The map itself can be presented in various formats, from simple hand-drawn sketches to sophisticated digital representations utilizing Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software.
The construction of a 70-mile radius map typically involves the following steps:
- Defining the Origin: The first step involves identifying the precise location that will serve as the center of the circle. This could be a city, a geographical landmark, or any other point of interest.
- Determining the Radius: The radius, in this case, is fixed at 70 miles. This distance can be adjusted based on the specific application and the desired scope of the map.
- Mapping the Circle: Using a suitable mapping tool, a circle with a 70-mile radius is drawn around the origin. This circle represents the boundary of the area encompassed by the map.
- Overlaying Data: The final step involves overlaying relevant data onto the map. This data can include anything from population density, road networks, natural resources, or even specific businesses or institutions located within the 70-mile radius.
Applications of 70-Mile Radius Maps
The versatility of 70-mile radius maps extends across various disciplines, offering valuable insights and facilitating informed decision-making in diverse scenarios. Here are some key applications:
1. Business and Marketing:
- Market Analysis: Businesses can utilize 70-mile radius maps to analyze potential markets within a specific geographic area. By overlaying demographic data, consumer spending patterns, and competitor locations, companies can identify growth opportunities, target marketing campaigns, and optimize distribution strategies.
- Site Selection: When choosing a location for a new store, warehouse, or other business facility, 70-mile radius maps can help evaluate factors like accessibility, proximity to customers, and availability of resources.
- Sales Territory Management: Sales teams can use 70-mile radius maps to define their territories, optimize route planning, and track sales performance within specific geographical areas.
2. Urban Planning and Development:
- Transportation Planning: 70-mile radius maps can be used to analyze transportation networks, identify potential congestion points, and evaluate the effectiveness of public transportation systems.
- Infrastructure Development: Planning for new infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, or power lines, can be informed by 70-mile radius maps that highlight existing infrastructure, population density, and environmental considerations.
- Community Development: Identifying areas within a 70-mile radius that require community development initiatives, such as affordable housing, healthcare facilities, or educational programs, can be facilitated by overlaying relevant data on the map.
3. Emergency Response and Disaster Management:
- Evacuation Planning: During natural disasters, 70-mile radius maps can be used to create evacuation routes, identify safe zones, and coordinate relief efforts.
- Resource Allocation: In emergency situations, 70-mile radius maps can help allocate resources effectively, ensuring that aid reaches affected areas promptly.
- Risk Assessment: 70-mile radius maps can assist in assessing potential risks associated with natural disasters, such as flooding, earthquakes, or wildfires, by overlaying data on terrain, population density, and infrastructure vulnerability.
4. Environmental Management:
- Habitat Conservation: 70-mile radius maps can be used to identify and map critical habitats for endangered species or ecosystems, facilitating conservation efforts.
- Pollution Monitoring: By overlaying pollution data, 70-mile radius maps can help monitor pollution levels, identify sources of contamination, and track the effectiveness of environmental regulations.
- Resource Management: 70-mile radius maps can be used to assess the availability of natural resources, such as water, timber, or minerals, and guide sustainable resource management practices.
5. Education and Research:
- Historical Research: 70-mile radius maps can be used to study historical events, analyze population movements, and understand the evolution of settlements over time.
- Geographical Studies: Researchers can use 70-mile radius maps to analyze geographical patterns, study the distribution of natural resources, and investigate the impact of human activities on the environment.
- Educational Tools: 70-mile radius maps can serve as engaging educational tools, helping students visualize geographical concepts, understand spatial relationships, and develop critical thinking skills.
Benefits and Challenges of 70-Mile Radius Maps
Benefits:
- Visual Clarity: Radius maps provide a clear and concise visual representation of the area within a specific distance from a central point. This visual clarity facilitates understanding and analysis.
- Data Integration: Radius maps allow for the integration of diverse datasets, providing a comprehensive overview of the area under study. This integration enables informed decision-making based on multiple factors.
- Scalability: Radius maps can be easily scaled to different distances, allowing users to adjust the scope of their analysis based on their specific needs.
- Accessibility: Radius maps are readily accessible, with various online tools and software readily available for their creation and use.
Challenges:
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of radius maps depends heavily on the quality and reliability of the underlying data. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to misleading results.
- Spatial Distortion: Depending on the projection used, radius maps can exhibit spatial distortion, particularly at larger scales. This distortion can affect the accuracy of distance measurements and the overall representation of the area.
- Oversimplification: Radius maps, by their nature, provide a simplified view of reality. They may not capture all the nuances and complexities of the area under study, potentially leading to overgeneralizations.
FAQs on 70-Mile Radius Maps
1. Why is a 70-mile radius often used?
The 70-mile radius is often used because it represents a reasonable distance for travel, commuting, and accessing services, particularly in areas with well-developed transportation infrastructure. This distance typically encompasses a significant portion of the surrounding area, providing a comprehensive view of the region.
2. Can I create a radius map for any distance?
Yes, you can create radius maps for any distance. The specific radius chosen will depend on the application and the desired scope of the analysis. For example, a smaller radius might be used for local planning, while a larger radius might be used for regional studies.
3. What types of data can I overlay on a radius map?
You can overlay various types of data on a radius map, including:
- Demographic data: Population density, age distribution, income levels, and educational attainment.
- Economic data: Business activity, employment rates, and consumer spending patterns.
- Transportation data: Road networks, public transportation routes, and traffic flow patterns.
- Environmental data: Land cover, water bodies, pollution levels, and natural hazards.
- Social data: Crime rates, healthcare facilities, and educational institutions.
4. Are there free tools available for creating radius maps?
Yes, there are numerous free online tools and software available for creating radius maps. Some popular options include Google Maps, ArcGIS Online, and Mapbox.
5. What are the limitations of radius maps?
Radius maps have several limitations, including:
- Spatial distortion: Depending on the projection used, radius maps can exhibit spatial distortion, particularly at larger scales.
- Data accuracy: The accuracy of radius maps depends heavily on the quality and reliability of the underlying data.
- Oversimplification: Radius maps provide a simplified view of reality, potentially leading to overgeneralizations.
Tips for Using 70-Mile Radius Maps Effectively
- Choose the appropriate radius: Select a radius that aligns with the scope of your analysis and the specific objectives you aim to achieve.
- Use high-quality data: Ensure that the data used to create the map is accurate, reliable, and up-to-date.
- Consider spatial distortion: Be aware of potential spatial distortion, particularly at larger scales, and take appropriate measures to minimize its impact.
- Use multiple layers: Overlay different layers of data to gain a comprehensive understanding of the area under study.
- Interpret results carefully: Avoid oversimplification and consider the limitations of radius maps when interpreting results.
Conclusion
70-mile radius maps, despite their apparent simplicity, offer a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing spatial data. Their versatility across various disciplines, from business and marketing to urban planning and environmental management, underscores their significance in decision-making processes. By understanding the underlying principles, applications, benefits, and challenges associated with these maps, individuals and organizations can effectively leverage their potential to gain valuable insights and make informed choices. As technology continues to evolve, the applications and capabilities of radius maps are likely to expand further, solidifying their place as essential tools for navigating and understanding our complex world.


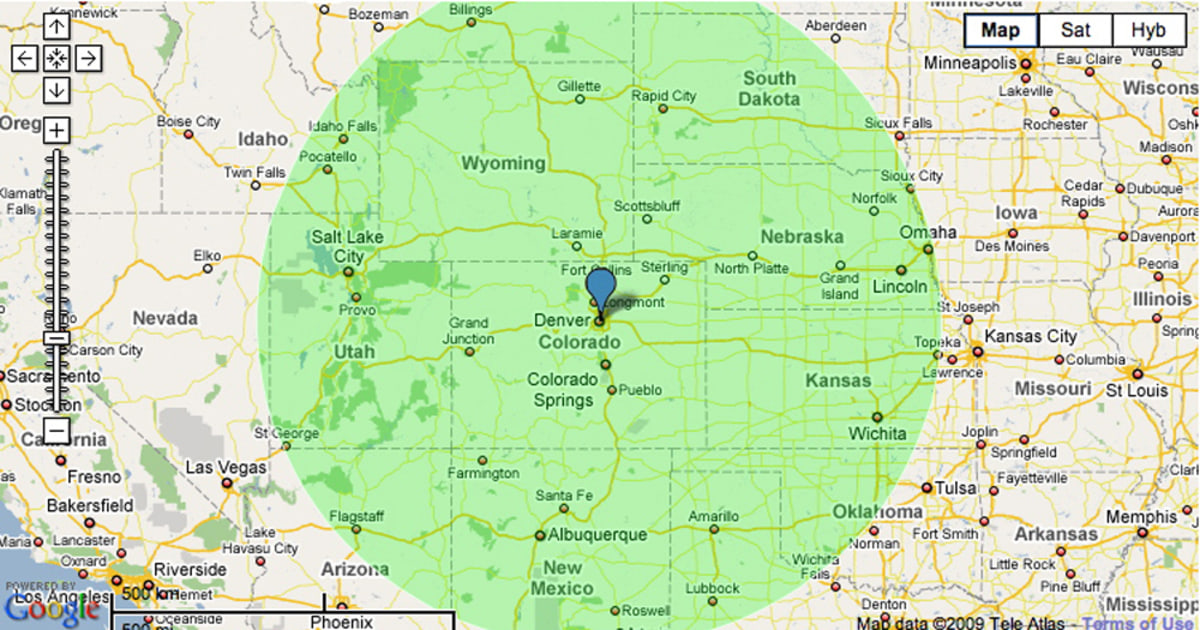



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World Within 70 Miles: A Comprehensive Guide to Radius Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
