Visualizing Proximity and Relationships: The Power of Overlapping Radius Circles on Maps
Related Articles: Visualizing Proximity and Relationships: The Power of Overlapping Radius Circles on Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Visualizing Proximity and Relationships: The Power of Overlapping Radius Circles on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Visualizing Proximity and Relationships: The Power of Overlapping Radius Circles on Maps
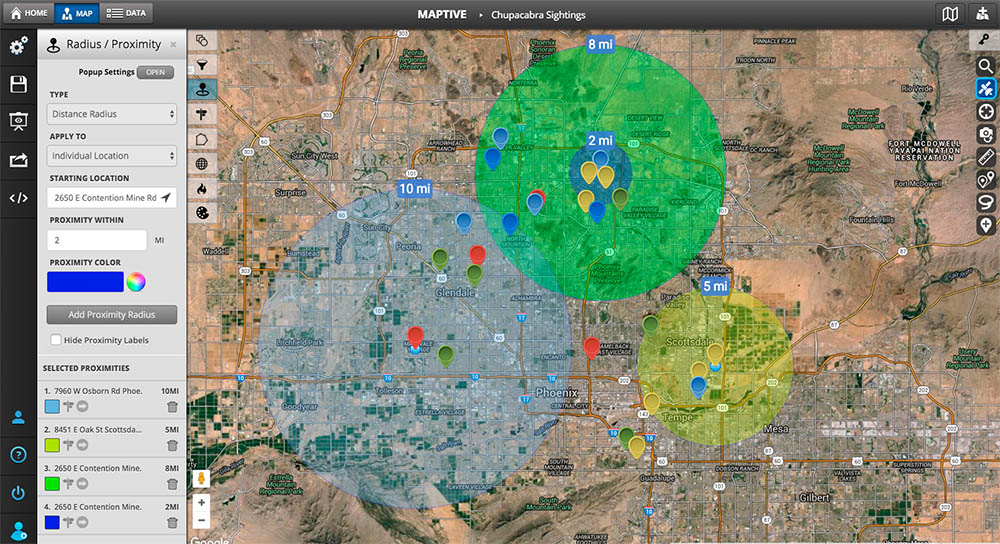
Maps are powerful tools for understanding spatial relationships and visualizing data. They can illustrate geographical features, population density, travel routes, and much more. However, a standard map often fails to effectively depict the concept of proximity or the influence of a specific location on its surroundings. This is where the technique of overlapping radius circles comes into play.
Overlapping radius circles, also known as "buffer zones" or "Voronoi diagrams," are a powerful visualization method that uses circles with varying radii to represent the influence or reach of a point of interest on a map. These circles overlap and intersect, creating a dynamic visual representation of spatial relationships and proximity. This technique is not merely a decorative element; it offers a unique perspective on data, revealing crucial insights that might be missed with traditional map representations.
Applications of Overlapping Radius Circles:
The application of overlapping radius circles extends far beyond aesthetic appeal. They serve as a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing various real-world scenarios, including:
-
Service Area Mapping: Visualizing the service areas of businesses, healthcare facilities, or emergency services. The radius of each circle represents the maximum distance a service can be provided, allowing for quick identification of potential coverage gaps or overlaps.
-
Influence Zones: Understanding the influence of specific locations, such as schools, shopping malls, or cultural landmarks. The radius can represent the distance people are willing to travel to access these facilities, highlighting areas of high and low influence.
-
Spatial Analysis: Analyzing the distribution and interaction of different entities, such as competing businesses, natural resources, or population clusters. Overlapping circles can reveal areas of high competition, resource scarcity, or population density.
-
Network Analysis: Visualizing the connectivity and reach of transportation networks, communication infrastructure, or power grids. The radius of each circle can represent the distance covered by a specific network element, highlighting potential bottlenecks or areas with weak connectivity.
-
Environmental Studies: Mapping the impact of environmental factors, such as pollution, deforestation, or climate change. The radius of each circle can represent the extent of the impact, revealing areas most vulnerable to environmental stressors.
Benefits of Using Overlapping Radius Circles:
The use of overlapping radius circles offers several distinct advantages over traditional map representations:
-
Enhanced Visual Clarity: The overlapping circles provide a clear and intuitive representation of the spatial relationships between points of interest, making it easier to understand the influence and reach of each location.
-
Data Visualization: Overlapping circles can effectively visualize complex data sets, such as population density, customer demographics, or resource distribution, by varying the size and color of the circles to represent different data values.
-
Interactive Exploration: Interactive maps with overlapping radius circles allow users to dynamically adjust the radii and explore different scenarios, enabling a deeper understanding of the data and its implications.
-
Decision Support: By visualizing proximity and influence, overlapping radius circles can provide valuable insights for decision-making in various fields, including urban planning, business strategy, and resource management.
Understanding the Mechanics of Overlapping Radius Circles:
To effectively utilize overlapping radius circles, it is crucial to understand the underlying principles and parameters involved:
-
Point of Interest: Each circle represents a specific location or point of interest, such as a business, a school, or a natural landmark.
-
Radius: The radius of each circle represents the distance of influence or reach of the corresponding point of interest. This radius can be based on factors like service area, travel time, or population density.
-
Color and Opacity: The color and opacity of the circles can be used to represent different data values, such as population density, service type, or risk level.
-
Overlap and Intersection: The overlapping and intersection of circles create areas of shared influence or proximity. These areas can be analyzed to understand the interplay between different points of interest.
-
Data Source: The data used to determine the radii and other parameters of the circles can come from various sources, such as geographic information systems (GIS), census data, or business records.
Creating Overlapping Radius Circles:
Creating overlapping radius circles on maps can be achieved using various software tools and techniques:
-
GIS Software: GIS software, such as ArcGIS, QGIS, or MapInfo, offers advanced tools for creating and analyzing overlapping radius circles, allowing for precise control over radii, colors, and other parameters.
-
Mapping APIs: Mapping APIs, such as Google Maps API or Leaflet, provide developers with the functionality to create custom maps with overlapping radius circles, integrating data from various sources and offering interactive features.
-
Spreadsheet Software: For simple applications, spreadsheet software like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets can be used to create basic overlapping radius circles using formulas and conditional formatting.
FAQs on Overlapping Radius Circles:
Q: How do I determine the appropriate radius for each circle?
A: The radius should be based on the specific context and data being visualized. For example, the radius of a service area circle might be determined by the maximum distance a service can be provided, while the radius of an influence zone circle might be based on the distance people are willing to travel.
Q: What are the limitations of using overlapping radius circles?
A: Overlapping radius circles can be visually complex, especially when dealing with a large number of points of interest. Additionally, the interpretation of overlapping areas can be subjective, requiring clear definitions and labels to avoid ambiguity.
Q: Can overlapping radius circles be used to visualize temporal data?
A: While primarily used for spatial data, overlapping radius circles can be adapted to visualize temporal data by varying the radius of the circles over time. For example, the radius of a circle representing a business could grow over time to reflect increasing customer reach.
Tips for Effective Use of Overlapping Radius Circles:
-
Clear Data Definition: Ensure that the data used to determine the radii and other parameters is accurate and well-defined.
-
Appropriate Radius Scaling: Choose a radius scaling that effectively represents the data and avoids excessive overlap or clutter.
-
Color and Opacity: Use color and opacity to differentiate between different data values and create visual hierarchy.
-
Interactive Features: Consider incorporating interactive features, such as zooming, panning, and tooltips, to enhance user experience and exploration.
-
Contextual Information: Provide clear labels, legends, and contextual information to guide users in interpreting the map and its data.
Conclusion:
Overlapping radius circles offer a powerful and versatile method for visualizing proximity, influence, and spatial relationships. By providing a clear and intuitive representation of data, this technique can enhance understanding, support decision-making, and unlock valuable insights in various fields. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of overlapping radius circles, further expanding their potential to illuminate the complexities of our spatial world.
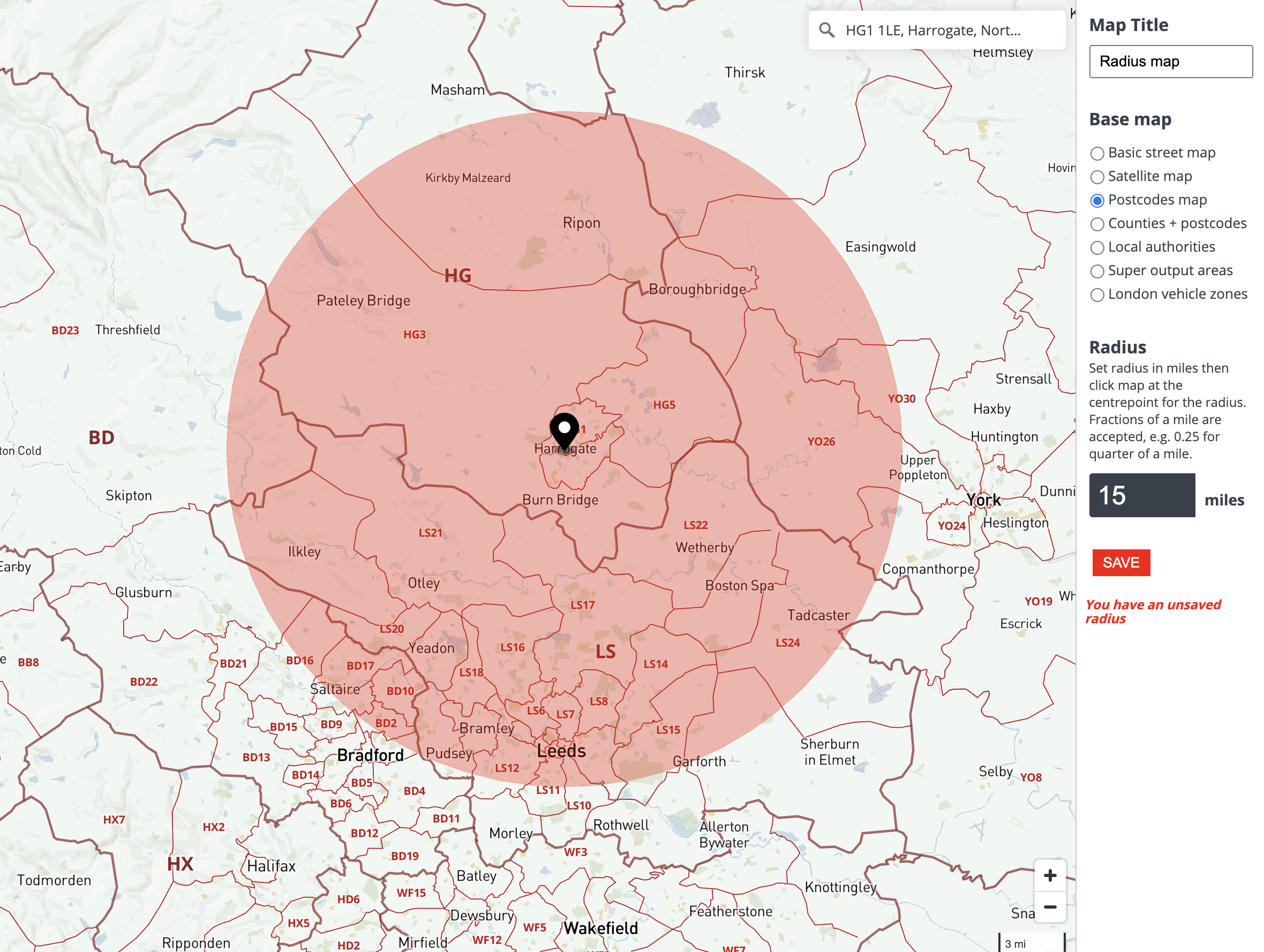


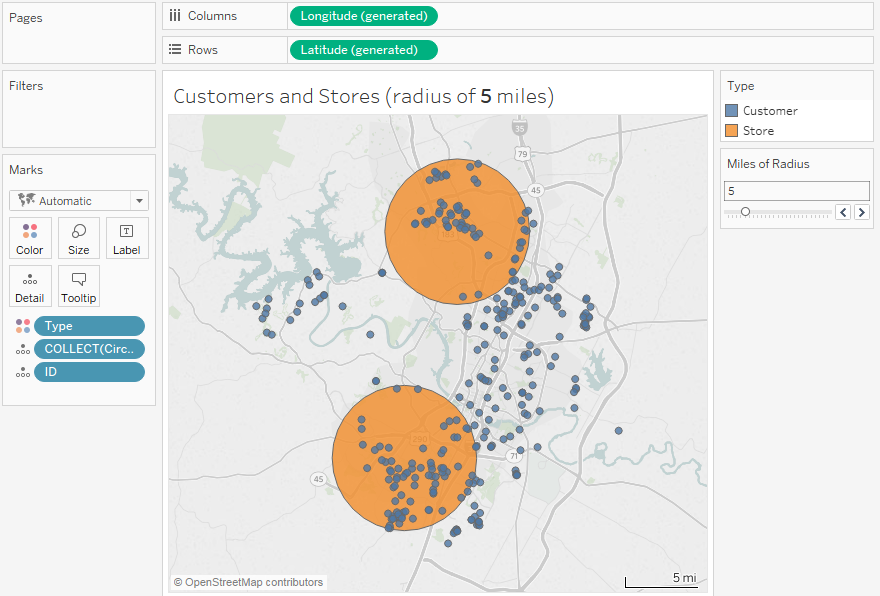

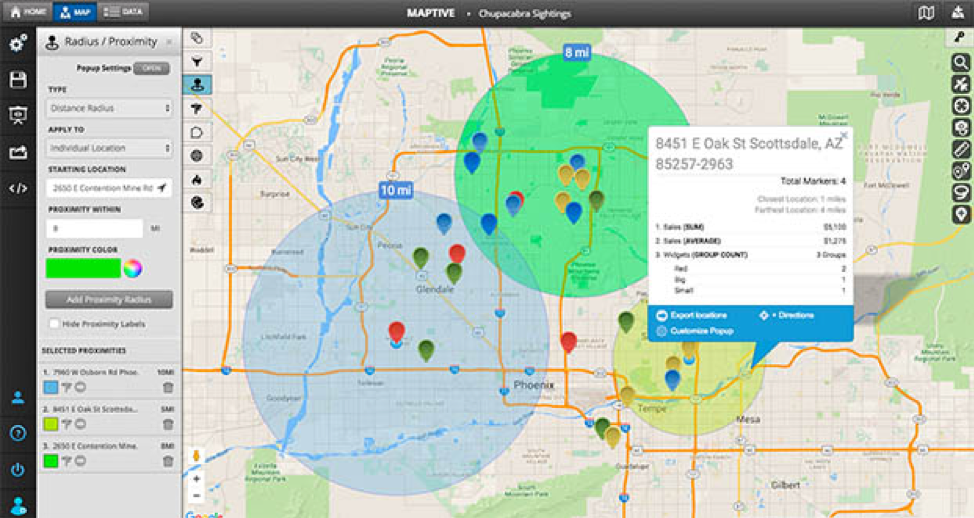

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Visualizing Proximity and Relationships: The Power of Overlapping Radius Circles on Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
